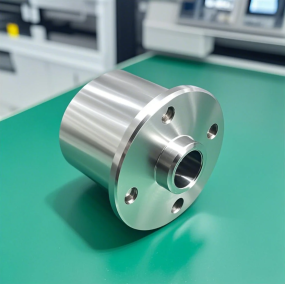
Do you really understand the methods of laser cutting?
Oxygen cutting: Oxygen, as an accelerant, can react violently with the metal heated by the laser to melt, generating a lot of oxidation heat, so in fact oxygen cutting is an "aerobic" version of melting cutting. Because metal combustion generates heat, oxygen cutting saves more energy than melting cutting, but the cutting speed is much higher than melting and vaporization cutting. Oxygen cutting is mainly used to cut carbon steel, titanium steel and other easily oxidized metal materials.
Scribing and controlled cracking: Scribing is the use of a high-energy density laser to scan the surface of a brittle material. After the material is heated, it evaporates into a small groove, applying a certain pressure to the material, causing the brittle material to crack along the small groove.
Controlled cracking is the steep temperature distribution produced by laser grooving, which generates partial thermal stress in brittle materials, causing the materials to crack along small grooves. For example, glass cutting.
The current use of laser cutting equipment in the market is divided into two categories: metal and non-metal.
It is a metal laser cutting machine used to make large equipment such as decoration, advertising, lamps, kitchen utensils, thin plates, electrical cabinets, elevator panels, engineering boards, and concave-convex switchgear.
Non-metallic laser cutters refer to equipment used to cut plastics (polymers), rubber, wood, paper products, leather, and natural or synthetic organic materials, because these items are not metal products and therefore absorb laser light differently. Therefore, this material is cut with a CO2 laser cutter.
Simply put, a laser is a focused beam of light that puts a lot of energy into a small area. When this happens, the material in front of the laser burns, melts, or vaporizes, forming a hole. Add some CNC to it and you get a machine that can cut or carve very complex parts made of wood, plastic, rubber, metal, foam, or other materials.



 English
English Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic French
French Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Malay
Malay Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latin
Latin Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque