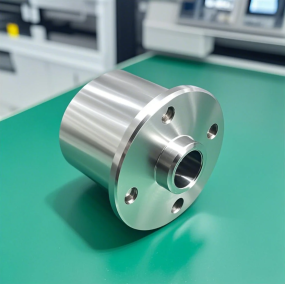
When machining automotive parts, in order to avoid deformation of parts, the following measures can be taken: 1. Rough machining and finishing are carried out separately to reduce the influence of cutting force and cutting heat, so that the deformation caused by rough machining can be corrected during the finishing process. 2. Reduce the influence of clamping force. The following measures can be taken in the machining process to effectively reduce the influence of clamping force on parts: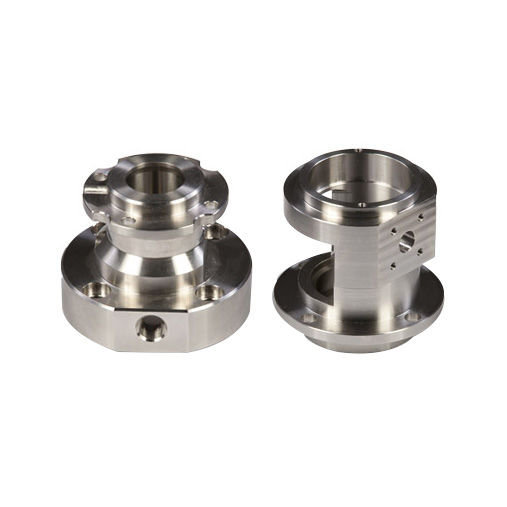  a. When radial clamping is used, the clamping force should not be concentrated on a certain radial section in the middle, but should be distributed over a larger area, so as to reduce the clamping force per unit area of the workpiece. If possible, install the workpiece in an open ring of appropriate thickness, and clamp it together with this ring. Special jaws that increase the contact area can also be used. If it is a hole positioning point, it is recommended to use both open spindle clamping. B. Change the clamping direction and change the radial clamping to axial clamping. C. The position of the clamping force should be selected in the position where the workpiece rigidity is relatively strong, so as to improve the deformation of the thin-walled parts under the action of the clamping force. d. Make a process boss or process thread to strengthen the rigidity on the workpiece to reduce the deformation caused by clamping. During processing, use a special structure of jaws to clamp, and then dispose of the boss or process thread after processing. 3. Use special fixtures to reduce clamping deformation. 4. Improve the quality of the blank. 5. Increase the stiffness of the parts to prevent excessive deformation. 6. Reduce the cutting force. In actual operation, the staff can flexibly apply the above measures according to the processing requirements and product characteristics to ensure the quality of automotive parts.
a. When radial clamping is used, the clamping force should not be concentrated on a certain radial section in the middle, but should be distributed over a larger area, so as to reduce the clamping force per unit area of the workpiece. If possible, install the workpiece in an open ring of appropriate thickness, and clamp it together with this ring. Special jaws that increase the contact area can also be used. If it is a hole positioning point, it is recommended to use both open spindle clamping. B. Change the clamping direction and change the radial clamping to axial clamping. C. The position of the clamping force should be selected in the position where the workpiece rigidity is relatively strong, so as to improve the deformation of the thin-walled parts under the action of the clamping force. d. Make a process boss or process thread to strengthen the rigidity on the workpiece to reduce the deformation caused by clamping. During processing, use a special structure of jaws to clamp, and then dispose of the boss or process thread after processing. 3. Use special fixtures to reduce clamping deformation. 4. Improve the quality of the blank. 5. Increase the stiffness of the parts to prevent excessive deformation. 6. Reduce the cutting force. In actual operation, the staff can flexibly apply the above measures according to the processing requirements and product characteristics to ensure the quality of automotive parts.
안녕하세요!EMAR 회사 웹 사이트에 오신 것을 환영합니다!
 Korean
Korean » »
» »
 English
English Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic French
French Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Malay
Malay Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latin
Latin Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque