1. Definition
Composite materials are new materials formed by optimizing and combining different properties of material components using advanced material preparation techniques. The general definition of composite materials requires the following conditions to be met:
(i) Materiales compositi artificiales et designae et fabricatae sunt secundum necessitates hominum;
(ii) Materiales Composite componentes ex duobus aut pluribus materialibus cum diversis proprietatibus chemicalis et physicis, combined in the designed form, proportion, and distribution, with clear interfaces between each component;
(iii) It has structural designability and can be used for composite structure design;
(iv) Composite materials not only maintain the advantages of the performance of each component material, but also achieve comprehensive performance that cannot be achieved by a single component material through the complementarity and correlation of the performance of each component.
Matrix materiae compositorum in duas categorias divisae sunt: metallici et non metallici. Substrati metalli usus sunt aluminium, magnesium, coper, titanium et alloys eorum. Non substrates metallici primarily include synthetic resins, ruber, ceramics, graphite, carbon, etc. Materiales principales reinforcing include glass fiber, carbon fiber, boron fiber, aramid fiber, silicon carbide fiber, asbestos fiber, whiskers, et metalla.

Classification
Materiales compositi mixture sunt. In multis regionibus, multos materiales tradicionales substituit. Materiales composite in metallum in metallum composite materialibus, non-metallum in metallum composite materialibus, non-metallum in non-metallo composite materialibus secundum compositum eorum. secundum characteres structurae eius, plus dividetur in:
[UNK]9312;Fiber reinforced composite materials. Differentes materiae fiber-reinforced inter matrices composite. Like fiber-reinforced plastics, fiber-reinforced metals, etc.
[UNK]9313;Laminated composite materials. Composed of surface materials and core materials with different properties. Usually, the surface material has high strength and is thin. lumen est et humilis est fortitudo et habet stipulatem et densitatem In duas species divisum est: sandwich solidum et sandwich melle.
[UNK]9314;Fine grained composite materials. Particula pulchra in matrice uniforme distribuere, sicut dispersione fermenta, ceramica metalla, etc.
[UNK]931515m;Hybrid composite materials. Composed of two or more reinforcing phase materials mixed in one matrix phase material. Compared with ordinary single reinforced phase composite materials, its impact strength, fatigue strength, and fracture difficulty are significantly improved, and it has special thermal expansion properties. Divided into intra layer hybrid, inter layer hybrid, sandwich hybrid, intra/inter layer hybrid, and super hybrid composite materiales.
Composite materials can be mainly divided into two categories: structural composite materials and functional composite materials.
Structural composite materials are materials used as load-bearing structures, which are basically composed of reinforcing elements that can withstand loads and matrix elements that can connect the reinforcing elements into a whole material while also transmitting forces. Fermentationes inter varios typos vitrorum, ceramicam, carbon, polymeros, metallos, etiam fibros naturales, fabrikas, whiskers, sheets, et particulas includent matrices polymeros (resinos), metallos, ceramicam, vitrum, carbon et cemento. Various structural composite materials can be composed of different reinforcing agents and matrices, and named after the matrix used, such as polymer (resin) based composite materials. The characteristic of structural composite material s is that they can be designed for component selection according to the requirements of the material's stress during use, and more importantly, composite structure design can also be carried out, that is, reinforcement arrangement design, which can reasonably meet the needs and save materials.
Materiales compositae functionalis generale compositus sunt ex componentibus functionalis corporis et matrices componentibus. Matrix non solum rolum in formatione totum, sed etiam functiones synergisticas aut reinforcing potest. Functional composite materials refer to composite materials that provide physical properties other than mechanical properties. Exemplo, conductivity, superconductivity, semiconductor, magnetism, piezoelectricity, damping, absorption, transmission, friction, shielding, flame retardancy, heat resistance, sound absorption, insulation, etc. highlight a certain function. Collectively referred to as functional composite materials. Materiales compositae functionalis principes ex corporibus functionis, corporibus et matrices reinforcing sunt. Corpus functionalis ex unas aut pluribus materialibus functionalis constituetur. Materiales multifunctionales compositos multiplicas functiones habere possunt. Meanwhile, it is also possible to generate new functions due to composite effects. Materiales multifunctionales compositae directa sunt materiae compositae functionalis.
Materiales compositi etiam in duas categorias divisi potest: usus utili et progressi.
Materiales commune composite, sicut fiberglass, low performance reinforcements, sicut vitra fibres et polymeros normal (resins) compositus sunt. Due its low price, it has been widely used in various fields such as ships, vehicles, chemical pipelines and storage tanks, building structures, and sports equipment.
Advanced composite materials refer to composite materials composed of high-performance heat-resistant polymers such as carbon fiber and aramid. Later, metal based, ceramic based, carbon (graphite) based, and functional composite materials were also included. Quamquam optima exercitus habent, precia eorum relative alta sunt, prima in defensione industria, aerospace, machina precisa, submersibla profunda maris, robot structural componentes, et equipa sportis altissima.
Application
Classificationes principales materiae compositorum sunt:
Dominus 9312;Aerospace agrus. Due to their good thermal stability, high specific strength, and stiffness, composite materials can be used to manufacture aircraft wings and forebodies, satellite antennas and their supporting structures, solar cell wings and shells, large launch vehicle shells, engine shells, space shuttle structural components, etc.
[UNK]9313;The automotive industry. Due to the special vibration damping characteristics of composite materials, they can reduce vibration and noise, have good fatigue resistance, are easy to repair after damage, and are easy to form as a whole. Therefore, they can be used to manufacture automobile bodies, load-bearing components, transmission shafts, engine mounts, and their internal components.
●9314;In fields of chemical, textile and machinery manufacturing. Materium compositum ex fibre carbon et matrice resina cum bono resistentia corrosionis, quod utilitur ad fabricandum equipationem chemicam, machinas textilias, machinas chartarum, copiarum, instrumentos machinarum velociter, instrumentos precisionis etc.
[UNK]931515;Medical field. Carbon fiber composite materiales excellentes proprietates mechanicales et non absorptio radiografiarum habent, et medicae X-ray machinae et orthopedici stenti fabricare poterunt. Carbon fiber composite materials also have biocompatibility and blood compatibility, good stability in biological environments, and are also used as biomedical materials. In addition, composite materials are also used for manufacturing sports equipment and as building materials.
4. Zirconium phosphate composite material modificatus
In recent years, polymer/inorganic layered nanocomposites have attracted widespread attention due to their excellent properties in various aspects. Numerous studies have shown that the mechanical and thermal properties of composite materials can be significantly improved with a small content of nano inorganic fillers. In hoc tempore multa studia sunt super nanocompositibus materiae inorganiorum, sicut montmorillonitis et attapulgitis cum polymer is, sed relative parva est exploratio super nanocompositibus polymerum/zirconium phosphatis.
La α - ZrP laminata habet structuram stabilem et potest sustinere laminatam relativamente stabilem etiam post introduccionem invitatis in interlayer. Est etiam magnam ion excambientiam capacitatem et constituentem rationem aspectorum constituabilem et distributionem dimensionis particularum angustam, ut adequat parare nanocompositis inorganis polymeros/layeros. To increase the interlayer spacing of zirconium phosphate, promote its delamination in the polymer matrix, and enhance the compatibility between zirconium phosphate layers and the polymer matrix, is required organic modification of a-ZrP. α - ZrP is generally modified with small molecule amines or alcohols through - OH protonation reactions or hydrogen bonding inside and outside their layers, and can also be intercalated with large molecules. However, due to the small interlayer spacing, it is difficult to directly intercalate large molecules, and usually requires small molecule pre support before exchanging with large molecules.
Salsa ammonium longa catena quaternaria (DMA-CMS) octadecyldimethylamine (DMA) et p-chloromethylstyrene (CMS) synthesizata sunt. α - ZrP prae methylamine suportata est et tunc DMA-CMS excambita est ut phosphate circonium organicamente modificata (ZrP. DMA. CMS) acciperet. Fosphate circonium organicamente tractatus est tunc congregata per PS ut praepararet nanocomposites phosphatis circonium PS/organicamente modificatae, et structura eorum et proprietates studiabant.
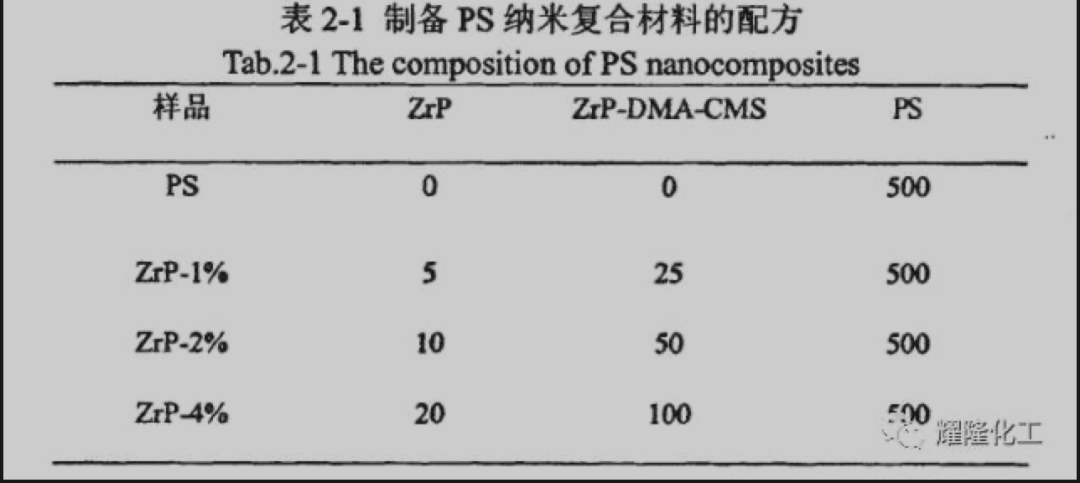
Examinatio XRD ostendet quod saltum amonium quaternarium longum catenam DMA-CMS relativamente facile est intrare inter layers α - ZrP post praepositum methylamine. Post interalationem distancia interlayer phosphate circonium ab 0,8 nm usque 4,0 nm crescit, et effectus interalationis significat. Materium nanocompositum paratum a extrusione ZrP DMA-CMS phosphate circonium modificatum (ZrP DMA-CMS) et PS ultra expandit interlayer spatiorem a 4.0 nm usque 4.3 nm in comparatione ZrP DMA-CMS, cum polystyrenem intrantem interlayer phosphatis zirconium.
Examinatio mecanica ostendet, quod quando contignatus phosphatis zirconiae 1%, fortitudo tensilis, modulus elastis, elongatio in pausa, et effectus nanocompositis phosphatis organicae PS/organicae modificatae circoniae multiplicabuntur per 4%, 21%, 8%, et 43%, respectively. But with the increase of zirconium phosphate content, the tensile strength, elastic modulus, elongation at break, and impact of nanocomposites show a downward trend, and the strength, rigidity and difficulty of the material begin to decrease. Additione adequatae summae phosphatae ZrP DMA-CMS circoniae modificatae organicae effecti fortitudinis et difficionis in PS habet.


 English
English Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German French
French Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Korean
Korean Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Malay
Malay Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque









