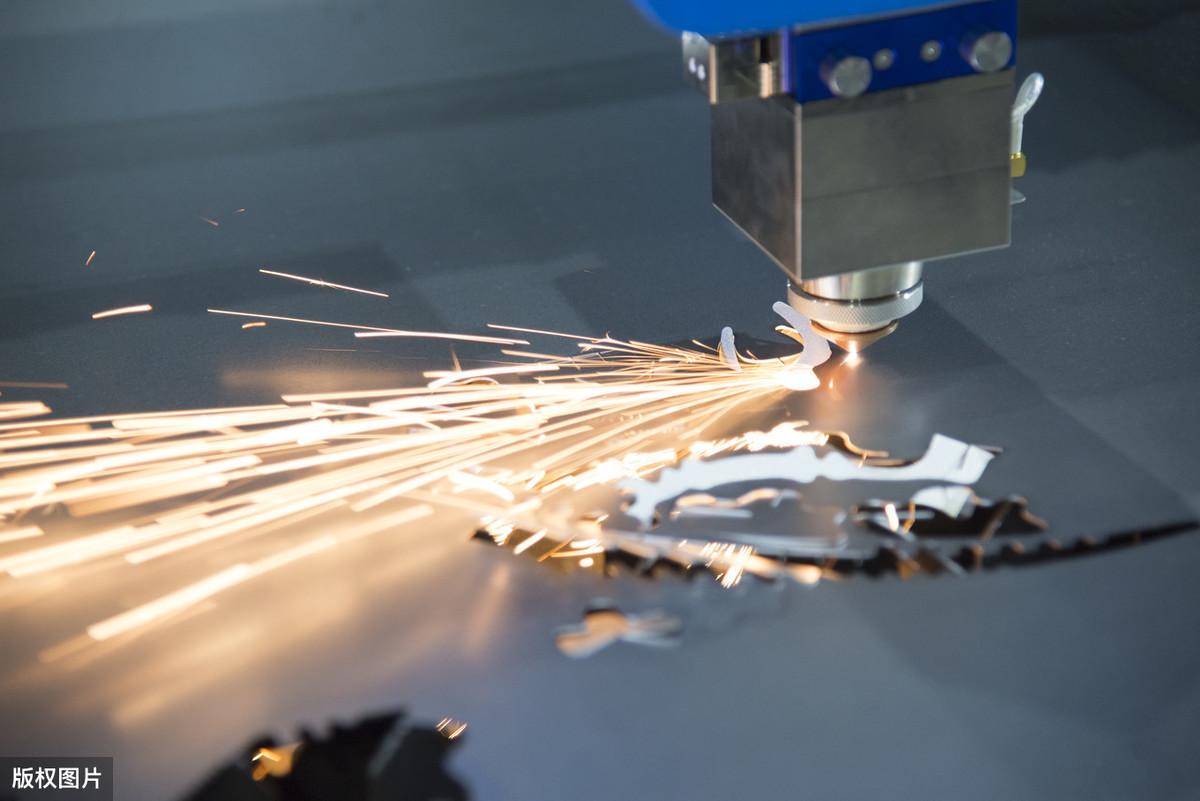
1) Laser vaporization cutting uses a high-energy density laser beam to heat the work piece, causing the temperature to rapidly rise and reach the boiling point of the material in a very short time. The material begins to vaporize, forming vapor. Velocitate eiectionis vaporis istis altissima est, et simul cum vaporis eiecti sunt, incisiones in materia formantur. Temperatur vaporization is materiae generale alta est, ergo vaporizatio laser magnam magnam magnam magnitudinem potentiae et densitatem potentiae requirit. Laser vaporization cutting is commonly used for cutting extremely thin metal materials and non-metallic materials such as paper, cloth, wood, plastic and rubber. 2) In laceribus absorbentibus, metallis fertur a calefactione laser is, et tunc non oxidising gases (Ar, He, N, etc.) effundentur per maculam coaxial cum trabeo, reliquus est super pressionem gasae fluctum ut discargat metallum liquidum et format succidendum. Laser contaminatio non potuit vaporizationem metalla completam, et solum 1/10 energiae requirit vaporizationis extinguere. Laser conflatio sublime utilitur ad succidendum materiae aut metallos active non facile oxidizatur, sicut steel stainless, titanium, aluminum et alloys eorum. 3) Principulus oxygeni laser is secationis similis est oxyacetylene secationis. Laser calamos fons et active gases, sicut oksijen, gases cut. Gas effudit reactionem metallo secentem causantem reactionem oxidationis et relevantem multam calorem oxidationis; On the other hand, blow the molten oxide and molten material out of the reaction zone to form a cut in the metal. A causa reaction is oxidationis during the cutting process, a large amount of heat is generated, so the energy required for laser oxygen cutting is only half of that for melting cutting, and the cutting speed is much faster than laser vaporization cutting and fusing cutting. Oxygenum laser sequitur primum facile ad materiales metallicos oxidizabilis, sicut ferrum carbonium, ferrum titanium, et ferrum tractatum ferrum. 4) Laser scribing and controlled fracture laser scribing use high-energy density lasers to scan the surface of brittle materials, causing the material to evaporate in a small groove when heated, and then apply a certain pressure, causing the brittle material to crack along the small groove. Laseri laser cutationis generale Q-switched lasers et CO2 lasers sunt. Controlling fracture is the use of the steep temperature distribution generated during laser grooving to create local thermal stress in brittle materials, causing the material to fracture along small grooves.



 English
English Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic French
French Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Malay
Malay Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Korean
Korean Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque