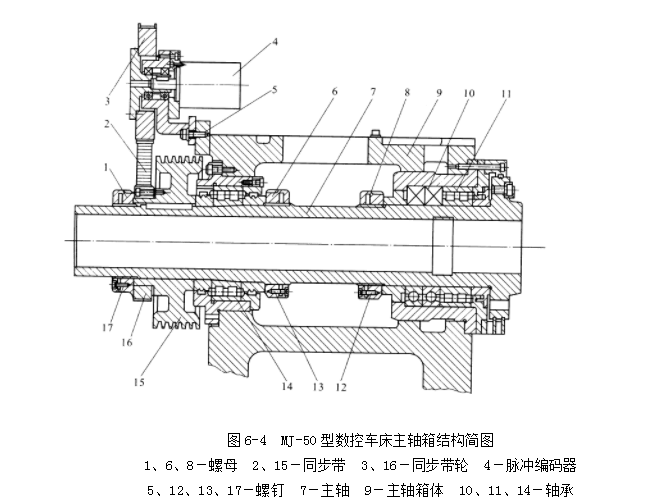
Ex altum diagramma structura componentium spindle centri CNC machinatorium verticali est. It consists of an automatic clamping and release mechanism for the spindle and cutting tools, as well as front and rear bearings. The front end of the spindle adopts a 7:24 taper hole, which is easy to install and remove the tool holder, and has a critical friction torque. The standard pull nail 5 is tighted inside the tool holder.
When it is necessary to tighten the tool, there is no oil pressure in the upper oil chamber of piston 1, and the spring force of the stacked spring 3 moves piston 1 up to the position shown in the diagram. Pull virgam 2 ascendit supra positionem monstratam in diagramma subter pressionem prima 3, et pila 4 fertur retracti et clampere in angulo anguli pullae pingis 5. Pull pingam 5 in supra per virgam pullae pilae steeli, ita ut superficie coni exterioris coni coni turris instrumenti et superficie coni interioris cavae spindle coni interiora concrimentur, et captor instrumenti clampetur in spindle.
When the handle is relaxed, hydraulic oil enters the upper oil chamber of piston 1, and the oil pressure causes piston 1 to move down, pushing rod 2 to move down. At this point, the stacked spring 3 is compressed, and the steel ball 4 moves downward along with the tension pin 5. When the steel ball moves to a larger spindle aperture, the tension pin 5 is released, and the tool and tension pin 5 can be removed by the robotic arm. Post manum roboticam novum instrumentum manum installatur, oleum hydraulicam in gazofilacio olei pistoni 1 facit pressionem et tenet instrumentum manum.
The handle clamping mechanism uses spring clamping and hydraulic relaxation to ensure that in the event of a sudden power outage during operation, the handle will not loose itself. Est aer compressus connectus ad summitatem partem virgae pistoniae. Quando brachium roboticam instrumentum ex spindle extractet, aer compressus pulsat rotam spindle per cinerem centram virgae pistoniae et pullat virgam, faciens superficiem virgae tenentis instrumenti conformatum in cinerem spindle, secundum rectam positionem instrumenti. Viatio 7 et 8 commutata sunt ut signalis mitterent ad clampionem et dissolutionem instrumentorum tenentem.


 English
English Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic French
French Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Malay
Malay Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Korean
Korean Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque