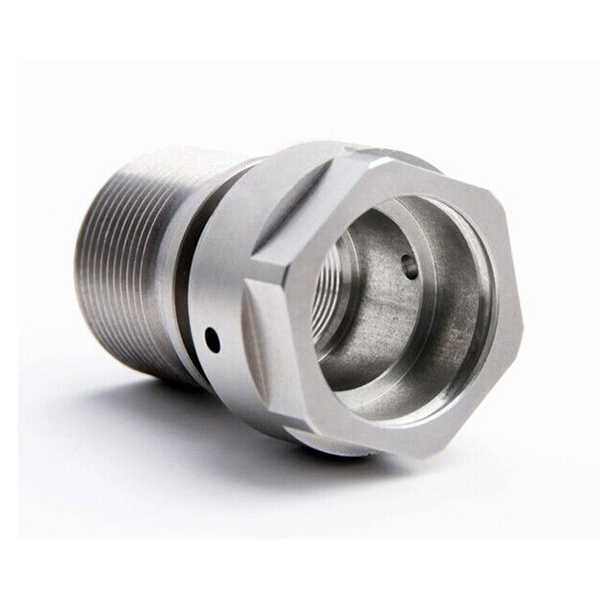
Titanium alloy CNC Machining is a complex process that involves multiple considerations and technical requirements. The titanium alloys have the characteristics of high strength, low thermal conductivity, low plasticity, high friction, and high chemical reactivity, which pose great challenges to processing. Therefore, CNC machining of titanium alloys requires the use of high-power, high torque CNC machining machines, as well as specially designed high-efficiency machining tools. The main reasons for tool damage during titanium alloy CNC machining are as follows: 0001. High temperature oxidation: Titanium alloy is prone to chemical reactions with oxygen in the air at high temperature, forming a high hardness oxide film, which can exacerbate tool wear. 2. Alta difficile: Titanium allocation habet altam difficilem, quod facit instrumentum cutationis maiorem faciem cutationis durantem procedentiam, quod facile potest inducere ad instrumentum laborem aut calciamentum. 3. Low thermal conductivity: Titanium alloys have poor thermal conductivity, and the cutting heat generated during processing cannot be dissipated in a timely manner, resulting in an increase in temperature in the cutting area and accelerating tool wear. 4. Parva elastica modulus: The elastic modulus of titanium alloy is small, and the surface rebound of the workpiece during cutting is large, which can easily cause increased friction between the back cutting surface of the tool and the workpiece surface, leading to tool wear. 5. High chemical activity: Titanium alloys have high chemical activity and are prone to chemical reactions with certain components in cutting fluids, leading to tool corrosion and wear.



 English
English Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic French
French Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Malay
Malay Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Korean
Korean Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque