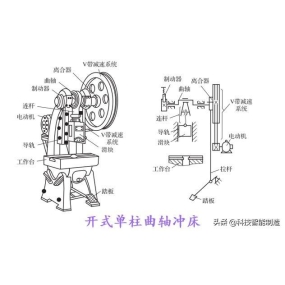
For companies engaged in precision machining, it should be clear that the process specification is the main technical document for the processing of aviation components. It specifies the process and sum of processing raw materials in qualified parts. Generally, the content of the process specification process chart includes equipment information, process equipment information, processing requirements, and operation steps. Operators of production only need to process the parts according to the order of the process chart in the process specification and the content in the process chart to process the raw materials into products that comply with the design drawings of Tonghu.
In update and iteration of aviation engines, the energy and reliability of engines are gradually improving. A single bright sword has more functions, and the structure of parts is becoming increasingly complex. The precision required for design is also increasing year by year. Model specializationis traditional process is no longer sufficient to meet the design requirements of engine components, as well as the production needs of high efficiency, high quality, and low cost. It is also not suitable for CNC Machining and information management. Exploring new process specification models and improving the current process specification situation are important issues that many engine component processing and technical personnel need to consider.
1 , Analysis of the Current Status of Component Processing Technology Regulations
The traditional mode of process specification is very simple, and the operation steps are not detailed enough. There are many uncertain factors that cannot guide the construction personnel well. Different operators have different introductions to the content of the process specification. The product quality and processing efficiency mostly depend on the operator. Compared with the international advanced aircraft engine specification mode, the gap is still quite obvious.
In the process specification, each processing step has a corresponding process chart. The traditional mode of process chart is relatively simple. The process chart mainly includes the schematic diagram of part processing, work content, the number of clamping molds, cutting tools, measuring tools used, the size and technical requirements that should be met after processing, and the matters that need to be noted. Taking the turning process as an example, Figure 1 is a chart of the part turning process. The sketch on the left is a schematic diagram of the machining process, usually represented by a two-dimensional view. The thick solid line represents the surface that needs to be machined, the thin solid line represents the non machined surface, and the uppercase letters A, B, C, etc. represent the positioning reference, support surface, clamping or pressing surface of the part. In diagramma schematicae, lineas dimensionales utiliuntur ad indicandum tolerantias dimensional is et positivas quae secundum superficiem machinatum impletam esse secutae sunt. Omnes dimensiones et tolerantias positivae numero secundum notae sunt. Contenium opus a dextris usus ex tres partes constituit. Primus parte ex necessitatibus alignationis ante processandum est. Usually requirit fixturam alignationis ut superficiem, superficiem radialem et superficiem axialem invenire, et maximum valorem executabilem indicat. Secundus est continens processionis in hoc processo, usus per numeros mensurae sequentibus, correspondentibus numeris sequentibus in diagramma machinae; Tertia est requisio formae et positivae tolerantiae post conversionem, quae correspondit ad numerum sequences in diagramma machinae.
1. Current situation of process specifications
Each machining process in the process specification has a corresponding process chart. The traditional mode of process chart is relatively simple. The process chart mainly includes the machining schematic diagram and work content of the components, the fixtures, molds, cutting tools, measuring tools, etc. used, the dimensions and technical requirements that should be met after completing the machining, and the key points that need to be noted.
2. Analysis of the Current Status of Process Regulations
1) Preparation analysis before processing
A prior processing, operators usually read the process chart. If it is a CNC machining process, they also need to read the CNC step card.materiae instrumentorum et dimensiones geometricae potent deviare. Parametri sequentes utili non rationabile sunt, resultant in qualitate superficie instabile et precision dimensional is parterum processentium, costas et cycles instabile processentium. Inaccurate tool consumption statistics make production preparation and implementation of production plans difficult. Similarly, when workers choose measuring tools, the measurement methods they use may also be inaccurate, and the accuracy of the selected measuring tools may not match the accuracy of the measured dimensions, resulting in inaccurate measurement results.
2) Analisi instaurationis fixtures and parts
For example, when installing fixtures and parts, the axis of the parts should be a s consistent as possible with the rotation center of the machine's worktable, and the cross section machine of the parts should be as perpendicular as possible to the rotation center of the machine's worktable, in order to ensure the mutual position requitant inter alia superficia eius post processionem. For parts that require high design accuracy, have relatively large dimensions, and are prone to deformation, the installation, calibration, et clamping steps of fixturis et partes sunt crucial, in quo erit signa magna impact on the machina precision parterum. A causa lack of installation views and operation steps for fixtures and parts in the process specification, machining personnel can only install fixtures and parts according to the process chart, sketch and simple calibration requirements in the work content column, Specificatio procedentis requirit ut exercitus interioris rotae partis non excedere 0,05mm ante processionem. Pro defectum correctionis claris punctis et continuae corrigentiae operantibus potest corrigentiam points-to-points aut continuam corrigentiam in processo operationis adopti. Point to point calibration requires a relatively short time and is easy to achieve, but the calibration results are not accurate. Continuous calibration requires a long time and is also difficult, but the calibration results will be more accurate. The two calibration methods will lead to essential differences in the machining results of the components. For the compression of parts, the process specification only specifies the use of pressure plates to compress the parts, without specifying the implementation steps, the magnitude of the compression force, and the precautions to be taken. Workers generally operate according to their own experience and habits, resulting in excessive or uneven compression force, which may cause damage or deformation to the parts.
3) Analisi procedentis processionis
When cutting parts, workers process them according to the size numbers in the job content column and the corresponding dimensions in the sketch. For cutting processes, workers arrange the machining sequence, cutting path, and cutting parameters of the part surface based on their own machining experience and habits. For CNC machining processes, CNC programmers arrange the above content based on their own process experience and habits. Due to the limitations and habitual thinking of machining personnel and CNC programmers in mastering mechanical machina, in machina machina, in conjuncting the machining sequence, cutting path, and cutting parameters of the part surface,via diferenta est, fortitudo succidit et concidit stressum generatum diferenta erit, et gradus instrumentorum vestitur et deformation is partee etiam differetur. Decisio est:. When the cutting parameters are different, the magnitude of cutting force, tool wear, machining quality of the part surface, and machining deformation of the part also vary.
Process specification sketches usually use two-dimensional views. For rotating parts and structurally simple parts, two-dimensional views can clearly express the structural shape of the parts. However, for parts with complex design mechanisms, surface designs with grooves, protrusions, and hole systems, or non rotating parts, they are generally machined on multi axis CNC machining centers, and two-dimensional views cannot clearly express these structural shapes and positional relationships.
2,Suggestiones for improvement measures of process specifications
Impressio modus specification is procedentis non solum simplicem meliorem stili mensae procedentis, sed inženieria systemae complexae multi faceted meliorissimae tecnologiae processionis. Sequentes sunt propositiones meliorissimae modi specificationis procedentis:
1. Refine the installation and adjustment of fixtures and parts
In diagramma procedentis specificationis procedentis, diagramma schematic a installationis fixturarum et parterum drawingi debet, detalior modos operationis et gradus specific pro fixtura et partibus installatione, calibracia et clampinda, ita ut omnes operatores secundum specificationem procedentis sine aliquid differentibus operare potest. Specificatio procedentis fixturae et partis installationis in parte conversationis gradus operationis specificat:
1) Uter oleum ut auferas protrusiones, ardores, et tummas super faciem operantis instrumenti machinae, et super terram lapidis. Wipe mundum cum veste mundo, pone plagam super faciem operantis instrumenti, alligat faciem radicalem currentem et finem de cylindro centro lapidis intra speciosa valoribus, et utilizat oleum ut auferat protrusiones et flammas super faciem superioris lapidis;
2) Lift fixture with the designated crane, remove any protrusions or burns on the installation ground with an oil, wipe it clean with a clean cloth, place the fixture on top of the pad, visually align the center, use the specified number of bolts to gently connect the fixture and pad, align the radial runout and end face flatness of the fixture within the specified values, tighten the bolts to fix the fixture to the worker, and then recheck that the radial and end face runout of the fixture should not exceed the specified values;
3) Wipe faciem part is et superficiem positionis fixturae mundam vestimento, inspice protrusiones, burres, etc., pone partem fixturae, allige intrinsecus delictum partis et salvum finis facis intra valorem specificatum, adjuste et tetigite suportum axialem in medio procedentis, tunc utilite numerum platearum presionis specificatum ut pulserant partem firmo, et tunc gauge dial ut verificere quod movetur superficie durante compressionem axialem intra valorem specificatum est;
4) Gently tight the radial anti movement bolts on the outer surface of the parts, without allowing them to move.
2. 3D machining view
With the continuous increase and update of the CNC equipment in various aviation enterprises, multi-axis CNC machines have been widely used for complex milling and hole machining processes. The machining process is mainly controlled by CNC programs. If the machining sketch of the process specification still uses a two-dimensional view, it cannot intuitively express the structural shape of the machining and the positional relationship between each machining part.procesus machinationis;
3. Planate the surface processing sequence and cutting path
In multis cases, sunt duas aut plures superficies machinae in processo, et omnes superficies machinae non sunt machinae in una iterum.via et direction, sequentibus principibus conducivi sunt ad controllendum deformation is, quae occurrit in parte machinaturae, vitam quaecumque instrumentorum superficie extendentem, et proceduram controllentem, ita ut qualitatem machinaturae, costum machinaturae, et circulum machinaturae relative stabile sunt;
4. Resources for improving process information
1) Cancella discipula CNC et integra informationes et informationes de programma CNC ab discipulis CNC in specifyationem procedentis. Hoc potest effectivus dimittere difficultatem gestionis ficorum procedentis et etiam eliminare complexitatem operatorum, qui necessari sunt ut et specifyationem procedentis et discipulis CNC simul proeliare.
2) Improve the information of cutting tools and measuring tools. In addition to the special cutting tool numbers marked in the process chart, the information of general cutting tools should also be indicated.instrumenta mensura etiam markentur;

iCalImp
In recent decades, the mode of processing technology regulations for the domestic aviation's compositions, in vitvitrum, in anianim, a anim hanc, a anim hanc, a anim hanc, a anim hanc, a anim hanc, a anim hanc, a anim hinc, a anim hinc, anim hinc, anim hinc, anim hinc, anim hinc, anim hinc, anim hinc, anim hinc, anim hinc, anim hinc, anim hinc, anim hinc, anim hinc, anim hinc, anim hinc, anim hinc, anim hinc, anim hinc, anim hinc, anim hinc, anim hinc, anim hinc, anim, anim hinc, anim hinc, motor aviation is domus.
A SanSanSana Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sina Sin Sina Sina Sin Exoptatus est ad nos vocare et vobis servire consecrati sumus


 English
English Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic French
French Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Malay
Malay Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Korean
Korean Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque