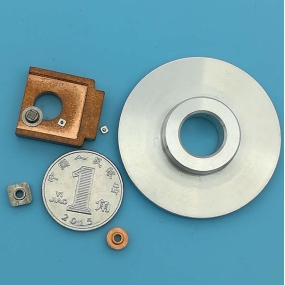
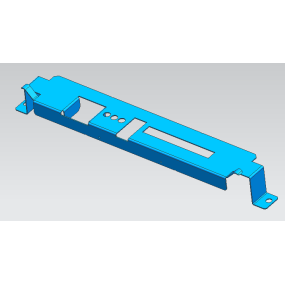
Summary of mechanical processing procedures and price estimation
1,Mechanical processing steps:
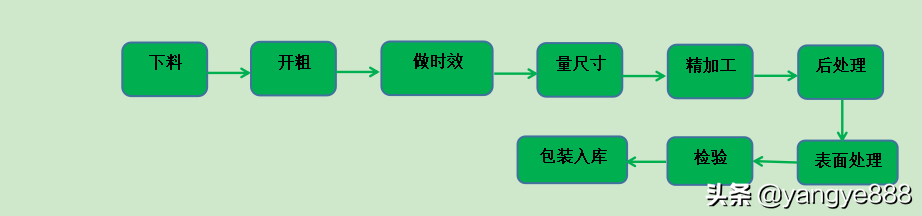
1) Cutting: Use a saw to cut the corresponding material in the approximate dimensions of the parts to be processed. (Generally, leave a margin of 5-8 mm for length and width)
2) Machinae difficile: Utrum apparatum, quasi latus, militias, et latus, ut dissipant formam difficilis partibus, quas a drawinge requirit, multum vacuum consentium auferunt.
3) Tempus efficibilitate: Tempus efficibilitate in naturam tempus efficibilitatem et artificiam tempus efficibilitatem dividitur. Natural aging refers to allowing the workpiece to stand for 24 hours or longer, while artificial aging refers to heat treatment of the workpiece in a high-temperature box or box furnace. The purpose of aging is to eliminate stress and reduce deformation of the workpiece during precision milling process.
4) Dimensio mensurae: Post senectionem, labor gradus deformation is subvertet, et mensura mensura est, ut determinaret mare.
5) Precision machining: Strictly follow the dimensions required by the drawing for precision machining to meet the dimensions of the workpiece required by the drawing. For workpieces with high precision requirements, semi precision machining processes will be arranged as needed before precision machining.
6) Post processionem: Haec processus intersperabitur in priorem processum dependente de typo partis.
1. Fitter: including chiseling, sawing, filing, correcting, drilling, threading, removing burrites, chamfering, and installing screws on workpieces.
2. Machina gravitationis: Quando alta precision est pro circulo exterior, intrinsecus cinerem et finem faciem operantis, necesse est relinquere marjinam post proceduram machinae precision et machinam gravitationis ad grindum.
3. Maquina confusa: For holas that require high precision in size, shape, and position, use a boring machine for processing.
4. Teste: Teste superficie necesse est pro utraque partes standardissimas et partes ferentes ut fortitudinem opus sit.
7) Surface treatment: After the completion of workpiece processing, surface treatments such as ordinary oxidation, pulse anodizing, hard oxidation, passivation, sandblasting, painting, etc. need to be applied to the workpiece surface to achieve aesthetic and anti oxidation effects.
8) Inspectio: Opus faciem tractatum est inspicere, includit informationes claves, quales dimensiones et colores, ut conformetur sculptilibus.
9) Packaging and storage: Package the inspected workpieces and store them together with the certificate of conformity, inspection report and other documents.
2,Composition of quotation for machined workpieces
1) Materials: Calculate material costs based on the density and price of materials required for different workpieces. ( ρ= M/v)
2) Working hours: mainly including manual operation hours and equipment processing hours, the price is calculated based on personnel hourly wages and equipment hourly fees * program running time. (Programmatio)
3) Pecunia operationis superficiis: Preces calculata est based on the different surface treatment processes required by the workpiece drawing.
4) Profit: According to the company's operation and scale, calculate the profit quotation proportionally based on the aforementioned prices.
5) Tax: Accounting for taxes based on the invoicing format and tax points required by the country.
6) Transportatio: Corresponding fees will be charged based on different transportation methods. (Exemplis freight air, logistics, express delivery, etc.)
3,Processus labor hours
Time required to complete a process, process hours=preparation hours+basic time
Tempus preparationis referit ad tempus consumptum a laboribus ad cognoscere se cum documentis procedentibus, vacuum accipere, fixturas instaurare, instrumenta machinae adjustere, positiones nullas alignere et fixturas disassemabiles.
Tempus basis est tempus accepit ut procederet programmam procedentis.
4,Quotation cost estimation method (this method is applicable to mass-produced products for reference)
Processing cost=(material cost+processing fee) * 1.2~1.5 (including management fee, sample and small batch coefficients * 3~5)
Material cost=weight (density * volume) * unit price (yuan/kg)
Processing fee=process hours * unit price (yuan/hour)
5、 Common aluminum and steel prices:
According to the manufacturer's announcement

8, 3D printing fee model
Usually charged based on the weight of the materials used (yuan/g) (additional fees will be charged if other treatments are required)
Preces materiae usus similes sunt:
9,Welding:
1) Vigilum ferrum ferrum ferrum: prima inter ferrum et ferrum ferrum ferrum utilium est. Laer oxideum super superficiem virgae ferri potest usar ad isolatum aerum et protegere trabem ferrum.
2) Second protection welding: using carbon dioxide as a shielding gas to protect the welding pass, with a thicker welding layer.
3) Argon arc a ferentia: Metodo ferentis amplius utilizatus est, qui gas argon in sculptilia utilizat ut protegeret passum ferentis. Temperatura ferentis alta est, et layer ferentis thina et firma est. Can be used for welding of steel, aluminum, and titanium alloys.
4) Laser welding: Laser high-temperature dissolution welding wire with weak firmness, mainly used for welding decorative parts.
5) Vacuum welding: In vacuum environment, argon arc a welding is used to weld, ensuring that the weld bead and workpiece are isolated from air and welding is reliable. Methodus principis titanium ferentibus.


 English
English Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German French
French Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Korean
Korean Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Malay
Malay Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque