Summary of Mechanical Processing Procedures and Price Estimation
1、 Mechanical processing procedures:
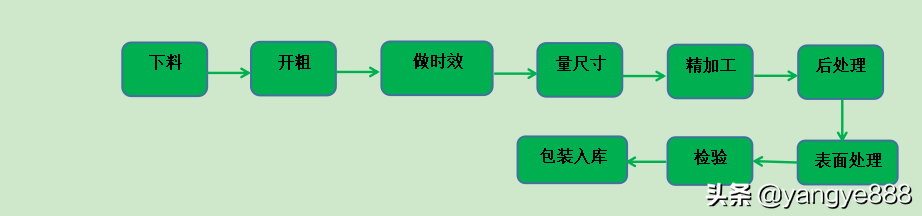
1) Cutting: Use a sawing machine to cut the corresponding material into the approximate size of the parts that need to be processed. (Usually leave a margin of 5-8mm in length and width)
2) Rough cutting: Use lathes, milling machines, wire cutting and other equipment to process the approximate shape of the parts required by the drawing, removing most of the blank allowance.
3) Timeliness: Timeliness is divided into natural timeliness and artificial timeliness. Natural aging refers to allowing the workpiece to stand for 24 hours or longer, while artificial aging refers to heat treatment of the workpiece in a high-temperature box or box furnace. The purpose of time efficiency is to eliminate stress and reduce deformation of the workpiece during precision milling process.
4) Measuring dimensions: After the aging process is completed, the workpiece will undergo some degree of deformation and needs to be re measured to determine the remaining amount.
5) Precision machining: Strictly follow the dimensions required by the drawing to carry out precision machining to meet the workpiece dimensions required by the drawing. For workpieces with high precision requirements, semi precision machining processes will be arranged as needed before precision machining.
6) Post processing: This process will be inserted into the previous process according to the different types of parts.
1. Fitter: including chiseling, sawing, filing, straightening, drilling, threading, deburring, chamfering, and screwing of workpieces.
2. Grinding machine: When high precision is required for the outer circle, inner hole, end face, etc. of the workpiece, it is necessary to leave a margin after the precision machining process and use a grinding machine for grinding.
3. Boring machine: For holes with high requirements for size, shape, and positional accuracy, use a boring machine for machining.
4. Flaw detection: Surface flaw detection is required for standard screw parts and welded parts to ensure the strength of the workpiece.
7) Surface treatment: After the processing of the workpiece is completed, surface treatments such as ordinary oxidation, pulse anodizing, hard oxidation, passivation, sandblasting, painting, etc. need to be applied to the workpiece surface to achieve the effect of aesthetic and oxidation prevention.
8) Inspection: It is necessary to inspect the surface treated workpiece, including various dimensions, colors, and other key information, to ensure compliance with the drawing requirements.
9) Packaging and storage: Packaging the qualified workpieces and storing them together with certificates of conformity, inspection reports, and other documents.
2、 Composition of quotation for machined workpieces
1) Materials: Calculate material costs based on the density and price of materials required for different workpieces. (ρ=m/v)
2) Working hours: mainly including manual operation hours and equipment processing hours, the price is calculated based on personnel hourly wages and equipment hourly fees multiplied by program running time. (Programming)
3) Surface treatment fee: Calculate the price based on the different surface treatment processes required by the workpiece drawing.
4) Profit: Based on the company's operation and scale, calculate the profit quotation proportionally on the aforementioned price basis.
5) Tax: Calculate taxes based on the invoicing format and tax points required by the country.
6) Transportation: Corresponding fees will be charged based on different transportation methods. (Examples include air freight, logistics, express delivery, etc.)
3、 Process working hours
The time required to complete a process, process hours=preparation hours+basic time
Preparation time refers to the time consumed by workers to familiarize themselves with process documents, collect blanks, install fixtures, adjust machine tools, align zero positions, and disassemble fixtures.
The basic time is the time it takes to process a process program.
4、 Quotation cost estimation method (this method is applicable to mass-produced products for reference)
Processing cost=(material cost+processing fee) * 1.2~1.5 (including management fee, sample and small batch factors * 3~5)
Material cost=weight (density * volume) * unit price (yuan/kg)
Processing fee=process hours * unit price (yuan/hour)
5、 Common aluminum and steel prices:
7075T6: Rod and Plate
Small factory: around 38 yuan/kg
Enterprise military standard: 96-100 yuan/kg
1. Dongqing Aluminum Industry:
National standard: 45-48 yuan/kg
National military standard: 78-80 yuan/kg
2. Southwest Aluminum Industry:
National standard: 52-60 yuan/kg
National military standard: 100+yuan/kg
2A12T4: Rod, Plate
1. Dongqing Aluminum Industry:
National standard: 40-45 yuan/kg
National military standard: 70-75 yuan/kg
2. Southwest Aluminum Industry:
National standard: 52-60 yuan/kg
National military standard: 100+yuan/kg
7075 tubes: around 75-80 yuan/kg; (Customization required, minimum order of 300kg)
2A12 pipes are 10-20 yuan/kg more expensive than bars and plates
6061 rods and plates: around 30 yuan/kg
6063 rods and plates: around 24-28 yuan/kg
7075 T7351/T7451: Around 80 yuan/kg
7050: Around 85 yuan/kg
Steel material:
45 #, Q235: The current average price is around 7.5 yuan/kg.
304 rods and boards: around 30 yuan/kg. About 20 yuan/kg in previous years
05cr17ni4: National standard: around 55 yuan/kg; National military standard: around 120 yuan/kg
30CrMnsiA: National standard: around 35 yuan/kg; National military standard: around 80 yuan/kg
1cr18ni9:26 yuan/kg or so
Pom (black, non flame retardant): around 15/kg
Brass: around 60/kg
6、 Quotation for commonly used processing equipment:
1) Ordinary lathe: 35-45 yuan/hour
2) CNC lathe: around 80 yuan/hour
3) 3-axis machining center: around 60-120 yuan/hour;
4) 4-axis machining center: around 150 yuan/hour; Batch price of 120 yuan/hour
5) 5-axis machining center: 300-500 yuan/hour
6) Grinding machine: 60 yuan/hour
7) Milling machine: 60 yuan/hour
8) Spark machine: 80~150 yuan/hour
9) Slow walking silk: 60-150 yuan/hour
10) Fitter: 80/hour
7、 Common surface treatment prices:
1) Ben, white oxidation: about 3 yuan/decimeter ²
2) Black oxidation: around 4 yuan/decimeter ²
3) Hard sulfuric acid anodizing: around 5 yuan/decimeter ²
4) Passivation: around 5 yuan/decimeter ²
5) Pulse anodizing: around 7.5 yuan/decimeter ²; By piece: Small items 5-10 yuan/piece
6) Sandblasting: around 1 yuan/decimeter ²
7) Spray painting: ordinary spray painting (without polishing or scraping putty): about 1 yuan/decimeter ²
Normal process painting: 3-3.5 yuan/decimeter ²
8) Nickel plating (chemical): 1.2 yuan/decimeter ²
9) Galvanized (white): 2-3 yuan/kg (workpiece weight)

8、 3D printing fee model
Usually charged based on the weight of the materials used (yuan/g) (additional charges may apply if other treatments are required)
The reference prices for commonly used materials are as follows:
9、 Welding:
1) Welding rod welding: mainly used for welding between iron and iron, the oxide scale on the surface of the welding rod can be used to isolate air and protect the weld bead.
2) Double protection welding: using carbon dioxide as a protective gas to protect the weld bead, with a thick weld layer.
3) Argon arc welding: The most widely used welding method, which uses argon gas as a protective gas to protect the weld bead. The welding temperature is high, and the weld layer is thin and firm. Can be used for welding steel, aluminum, and titanium alloys.
4) Laser welding: Laser high-temperature dissolution welding wire, with weak firmness, mainly used for welding decorative parts.
5) Vacuum welding: Welding is carried out in a vacuum environment using argon arc welding to ensure that the weld bead and workpiece are isolated from air and the welding is reliable. The main method for welding titanium alloys.


 Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic French
French Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Malay
Malay Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Korean
Korean Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latin
Latin Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque










