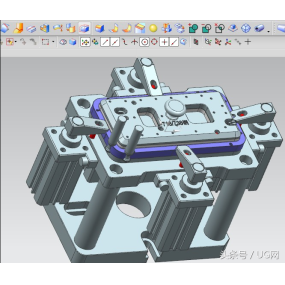
The process flow of Sheet Metal Processing refers to the entire process of gradually changing the shape, size, material properties, or assembly and welding of parts in a predetermined order during the production process, until a sheet metal part that meets the shape and size requirements is manufactured. For more complex structural parts, their production and processing generally require many processes such as material preparation, unfolding and layout, cutting blanks, forming, and assembly to be completed. Additionally, cold sheet metal processing is often combined with welding, metal cutting, heat treatment, and inspection processes to form a complete product manufacturing process.

Process specifications for sheet metal processing
The process flow specifies the machining process of the parts, while the specific machining content is guided and controlled by the process specification.
Process specification is a technically feasible and economically reasonable process plan selected by process technicians based on the requirements of product drawings, the characteristics of the workpiece, production batch, and the existing equipment and production capacity of the enterprise. After careful comprehensive analysis and comparison of several possible process plans, it is a technical document that guides the production process of parts. In the technical document, the blank used for the part, its processing method, and specific processing dimensions are specified; The nature, quantity, sequence, and quality requirements of each process; Equipment models and specifications used in each process; The form of processing tools (such as auxiliary tools, cutting tools, molds, etc.) used in each process; Quality requirements, inspection methods, and requirements for each process.
Generally speaking, when it comes to the processing technology of all sheet metal parts, it is often not completed by a single cutting and stamping workshop. Many parts may also be interspersed with mechanical processing, heat treatment, surface treatment, etc. Cross workshop and cross department operation guidance is controlled by their corresponding process specifications. However, in different industries, especially when processing sheet metal components with low professional technical requirements and low complexity, a comprehensive process specification is often compiled to guide production.


 Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic French
French Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Malay
Malay Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Korean
Korean Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latin
Latin Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque