CNC (Computer Numerical Control) is a CNC Machining technology controlled by a computer, which can achieve high-precision and high-efficiency machining processes. The principle and technology of CNC machining are as follows: 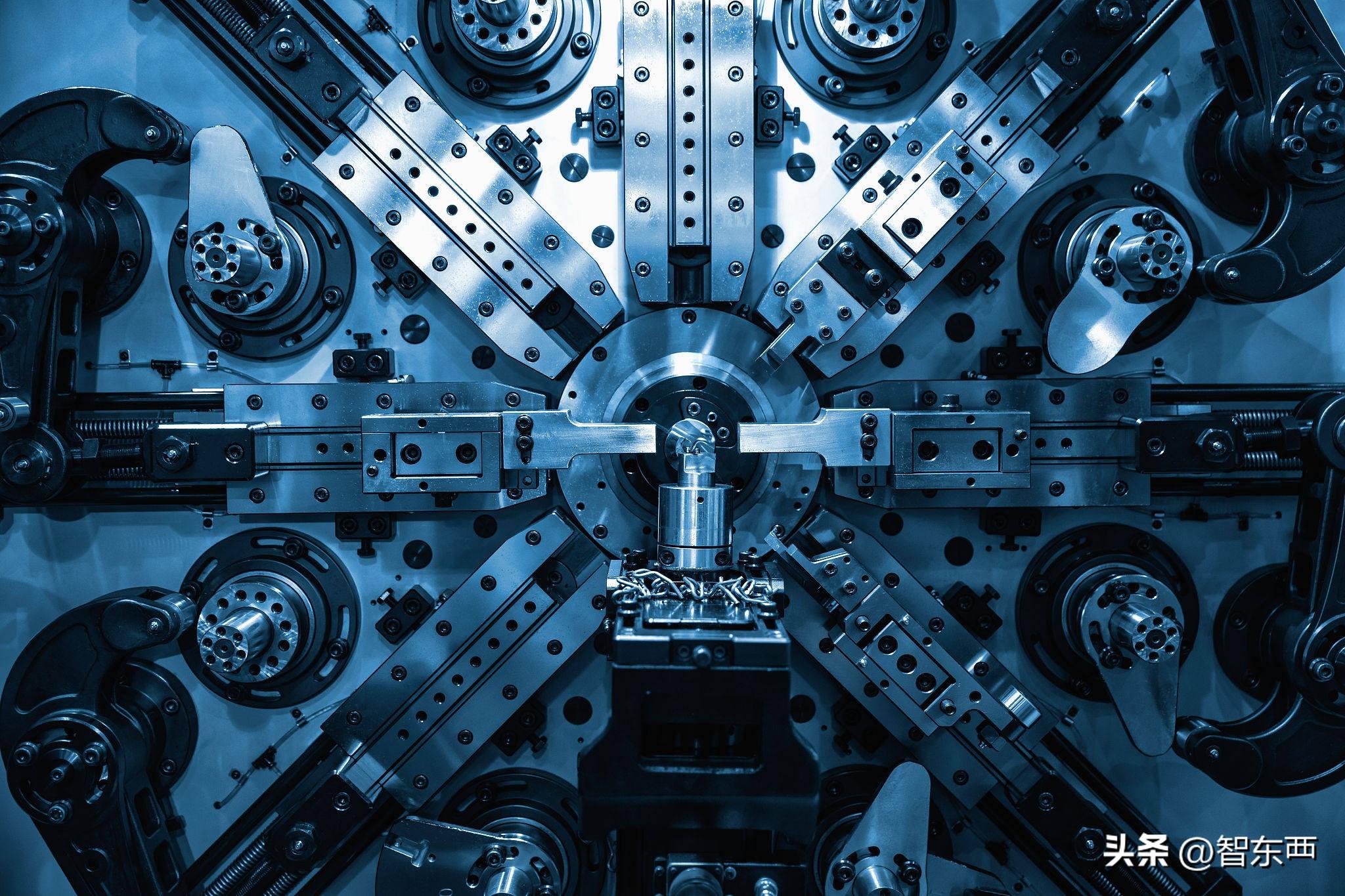
1. Numerical control programming: Firstly, it is necessary to write machining programs using specialized numerical control programming software. The machining program includes information such as machining path, cutting parameters, tool path, etc.
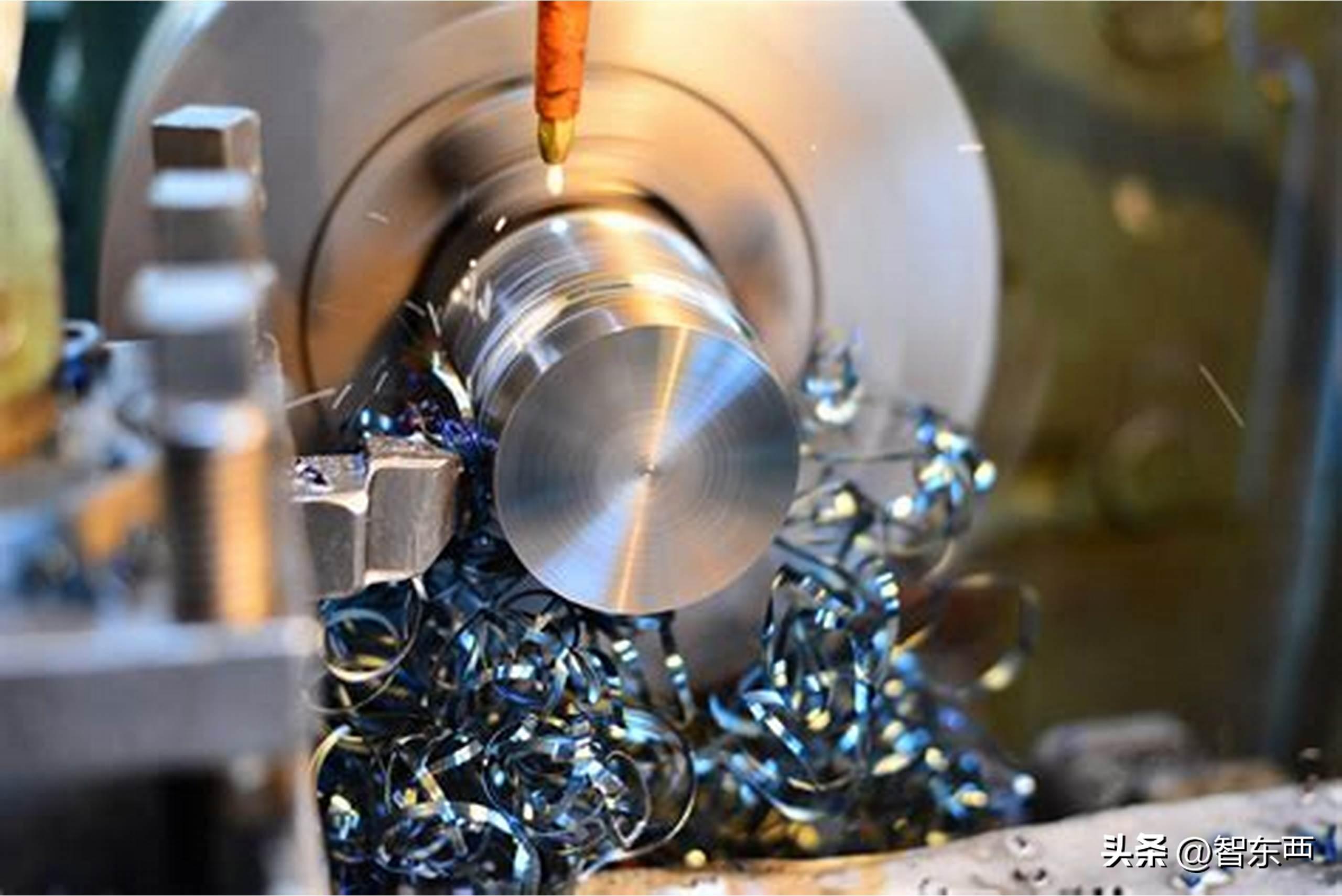

2. Machine tool control: The pre written machining program is loaded into the control system of the CNC machine tool. The control system controls various power components on the machine tool, such as the spindle, feed axis, and cutting tools, through the computer based on program instructions to achieve machining operations.
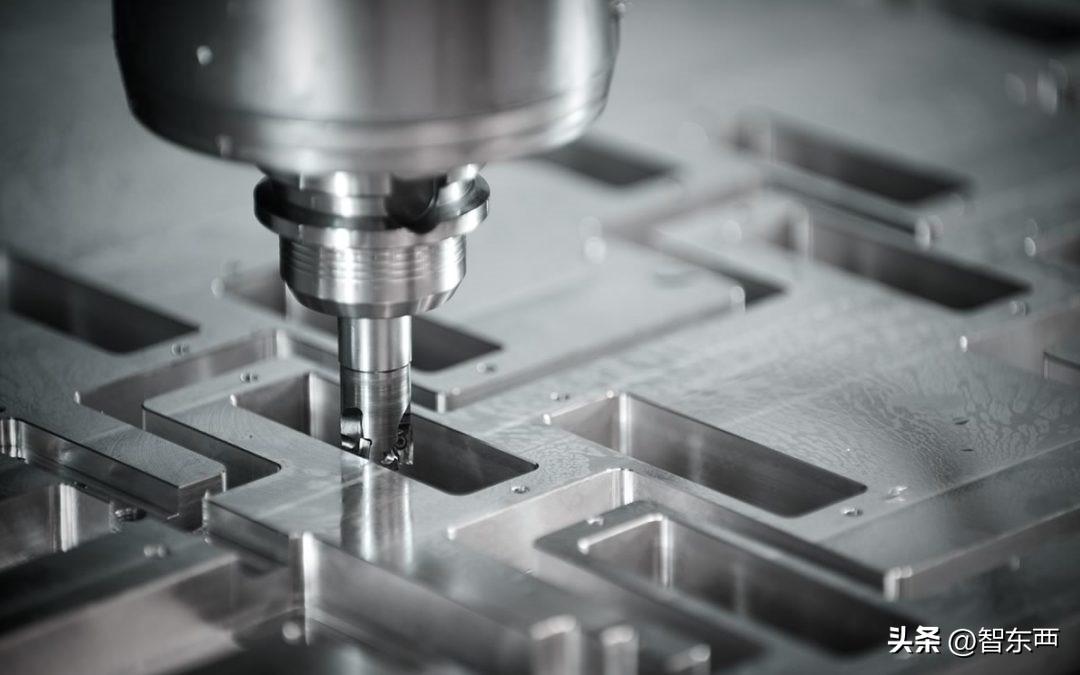

3. Machining process: During the machining process, the machine tool processes according to the path and cutting parameters specified in the machining program. The control system controls the movement and cutting speed of the tool according to program instructions, gradually cutting the raw material into the desired shape of the workpiece.
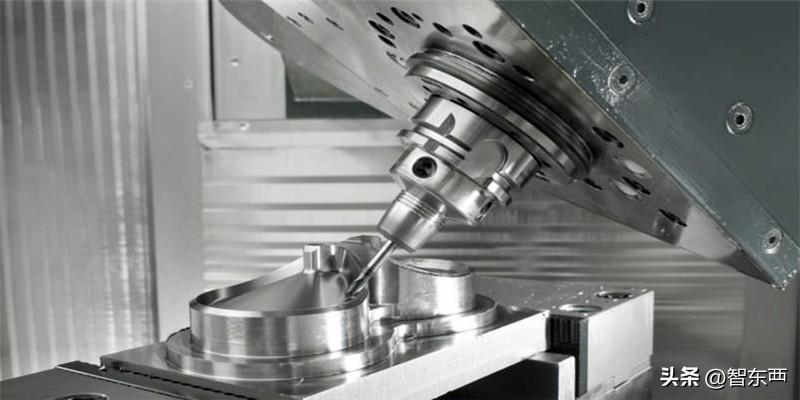

4. Automation control: CNC machining can achieve automation control. Through pre written machining programs, machine tools can automatically perform machining operations, reduce manual intervention, and improve production efficiency and machining accuracy.

As for the number of axes, it represents the degree of freedom of motion and machining capability of the CNC machine tool. Common CNC machine tools have different numbers of axes such as 3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis, etc. The more axes there are, the greater the degree of freedom of the machine tool in space, enabling more complex machining operations.
-3-axis machine tools: typically have three axes, X, Y, and Z, representing horizontal, vertical, and longitudinal motion, respectively. Suitable for flat and simple three-dimensional processing.
-4-axis machine tool: Adding a rotating axis on top of the 3-axis, usually rotating around the Z-axis. It can achieve rotational machining of workpieces.
-5-axis machine tool: Adding a tilt axis on top of the 4-axis, it can achieve tilted machining of workpieces. Can be used for processing complex surfaces, such as automotive parts, aircraft parts, etc.

The more axes there are, the stronger the machining capability of the machine tool, which can achieve more complex and precise machining operations. However, at the same time, an increase in the number of axes will also increase the complexity and cost of the machine tool. The selection of the appropriate number of axes needs to be determined based on specific processing requirements and budget.


 Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic French
French Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Malay
Malay Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Korean
Korean Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latin
Latin Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque











