What are the classifications of Metal Stamping molds? EMAR Precision will give you a brief introduction. For metal stamping molds, we can simply divide them into three types: engineering molds, conformity molds, and continuous molds. These are several commonly used molds in metal stamping factories. Below, we will briefly introduce these three types of molds:
Metal stamping parts
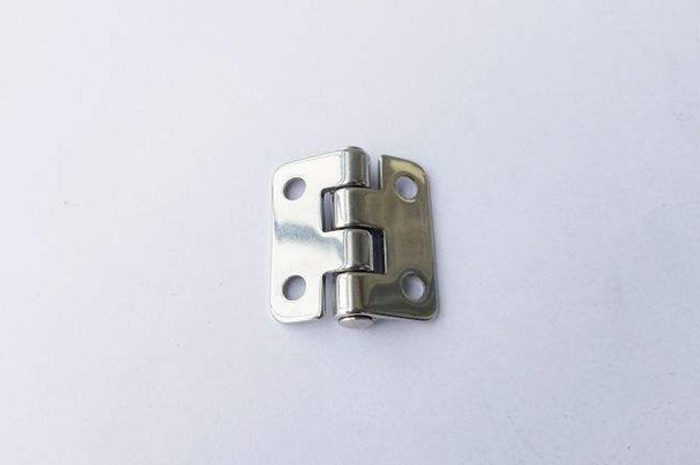

Engineering mold: This type of metal stamping mold requires manual or robotic labor to remove the product from the mold and place it in the next mold to continue production until one process of the mold is completed, and the entire product is considered complete. Maintenance is relatively simple, but manufacturing is time-consuming and labor-intensive, requiring a lot of labor and time costs, and the product scrap rate is high.
Composite mold: This type of metal stamping mold has a different structure from other engineering molds. Its punch is designed in the lower mold, and the other templates are the lower clamping plate (fixed convex mold), lower blocking plate, and lower stripping plate (stripping) in sequence. The upper mold is composed of a mother mold (or cutting edge), an inner stripping plate, and an upper backing plate in sequence. The stripping is hung on the upper backing plate with an equal height sleeve, and then supported by a rod or spring. For example, in the composite mold used for punching, the inner stripping is generally 0.50mm away from the mother mold and cannot be lower than the mother mold, otherwise the edge of the mother mold is prone to chipping or cannot be detached.
Metal stamping parts
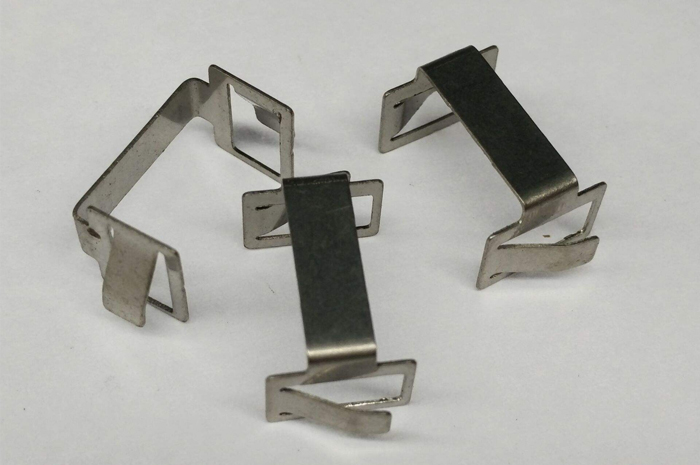
Continuous mold: This type of metal stamping mold is difficult to maintain and requires experienced assembly workers to operate, but it has high production efficiency. If the punching is fast, thousands of metal stamping products can be produced in an hour, saving labor and time costs, and the product scrap rate is low.


 Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic French
French Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Malay
Malay Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Korean
Korean Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latin
Latin Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque











