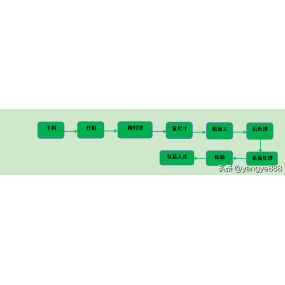
There are multiple difficulties in the CNC Machining process of titanium alloys, mainly due to the special physical and chemical properties of titanium alloy materials. The poor thermal conductivity of titanium alloy makes it difficult for cutting heat to diffuse during cutting, which leads to a rapid increase in tool temperature and subsequently causes rapid wear and cracking of the tool. This not only shortens the service life of the tool, but may also lead to tool collapse during the machining process, increasing machining costs and risks. The low elastic modulus and large elastic deformation of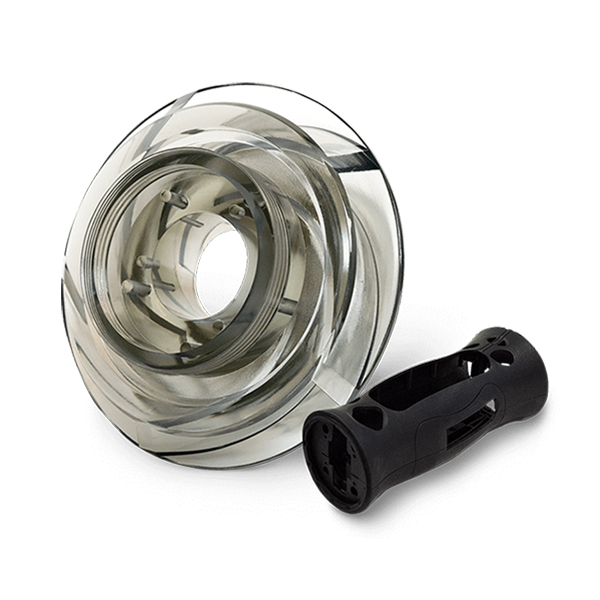  titanium alloy make it easy for the workpiece to rebound during processing, increasing the friction between the tool and the workpiece and further exacerbating tool wear. In addition, changes in cutting pressure may also cause vibrations in the workpiece, affecting machining accuracy and surface quality. Titanium alloys have high chemical reactivity and are prone to react with tool materials, leading to increased wear of the tools. This chemical wear not only affects the service life of the tool, but may also have a negative impact on machining accuracy and surface quality. The cutting machinability of titanium alloy is also poor, which is prone to chip accumulation and tool sticking, which may lead to increased cutting force and cutting temperature, further exacerbating tool wear and collapse. To overcome these difficulties, a series of measures need to be taken. For example, selecting appropriate tool materials and cutting parameters, optimizing cutting processes, reducing cutting temperatures and cutting forces; Using methods such as coolant processing and vibration processing to improve processing conditions; And design fixtures and clamping methods reasonably to reduce the vibration and deformation of workpieces during the machining process.
titanium alloy make it easy for the workpiece to rebound during processing, increasing the friction between the tool and the workpiece and further exacerbating tool wear. In addition, changes in cutting pressure may also cause vibrations in the workpiece, affecting machining accuracy and surface quality. Titanium alloys have high chemical reactivity and are prone to react with tool materials, leading to increased wear of the tools. This chemical wear not only affects the service life of the tool, but may also have a negative impact on machining accuracy and surface quality. The cutting machinability of titanium alloy is also poor, which is prone to chip accumulation and tool sticking, which may lead to increased cutting force and cutting temperature, further exacerbating tool wear and collapse. To overcome these difficulties, a series of measures need to be taken. For example, selecting appropriate tool materials and cutting parameters, optimizing cutting processes, reducing cutting temperatures and cutting forces; Using methods such as coolant processing and vibration processing to improve processing conditions; And design fixtures and clamping methods reasonably to reduce the vibration and deformation of workpieces during the machining process.
Hello! Welcome to EMAR's website!
 English
English » »
» »
 Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic French
French Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Malay
Malay Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Korean
Korean Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latin
Latin Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque