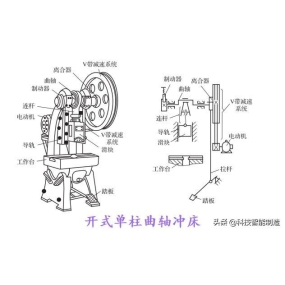
Common process flow of Sheet Metal Processing
1 The selection of materials for sheet metal processing generally includes cold-rolled sheet metal (SPCC), hot-rolled sheet metal (SHCC), galvanized sheet metal (SECC, SGCC), copper (CU), brass, purple copper, beryllium copper, aluminum plates (6061, 6063, hard aluminum, etc.), aluminum profiles, stainless steel (mirror, brushed surface, matte surface). The selection of materials varies depending on the product‘s function, and generally needs to be considered based on its purpose and cost.
1. Cold rolled SPCC sheet is mainly used for electroplating and baking paint parts, with low cost, easy molding, and a material thickness of 3.2mm.
2. Hot rolled plate SHCC, material T3.0mm, also uses electroplating and baking paint parts, with low cost but difficult to form, mainly using flat parts.
3. Galvanized sheet SECC SGCC. SECC electrolytic plates are divided into N material and P material. N material is mainly not surface treated and has a high cost, while P material is used for spraying.
4. Copper; Mainly using conductive materials, the surface treatment is nickel plating, chromium plating, or no treatment, which is costly.
5. Aluminum plate; Generally, surface chromate (J11-A) is used for oxidation (conductive oxidation, chemical oxidation), which is costly. Silver plating and nickel plating are available.
6. Aluminum profiles; Materials with complex cross-sectional structures are widely used in various plug-in boxes. Surface treatment is the same as aluminum plate.
7. Stainless steel; Mainly used without any surface treatment, high cost.
2 To review the drawings and write the process flow of the parts, it is necessary to first understand the various technical requirements of the part drawings; The review of drawings is the most important step in writing the process flow of parts.
1. Check if the drawing is complete.
2. The relationship between the drawing and view, whether the annotations are clear and complete, and the units of dimension annotations.
3. Assembly relationship, key dimensions required for assembly.
4. Differences between old and new layouts.
5. Translation of foreign language images.
6. Conversion of table codes.
7. Feedback and handling of graphic issues.
8. Materials
9. Quality requirements and process requirements
10. The official release of drawings must be stamped with a quality control seal.


 Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic French
French Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Malay
Malay Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Korean
Korean Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latin
Latin Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque