A Brief Discussion on CNC Machining "style=" font size: 18px; text-decoration: underline; Process analysis and planning of CNC machining
Programming process analysis and planning mainly include three major parts: processing object and processing area planning, processing process route planning, and processing process and processing method planning.
1. Planning of processing objects and processing areas
Dividing the processing object (workpiece) into different areas and using appropriate (different) processing techniques and methods for processing is aimed at improving processing efficiency and surface quality.
There are several common types of partitioned machining: (1) When the machining surface shape of the workpiece varies greatly, it is necessary to perform partitioned machining. (2) When there is a significant difference in the required precision and surface roughness for surface processing. (3) When there is a significant difference in size between different areas of the processed surface.
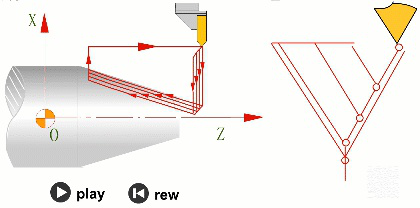
2. Planning of processing technology route
When designing the CNC process route, priority should be given to arranging the machining sequence, which should be comprehensively considered based on the structure of the parts, the shape of the blank, and the requirements for positioning, installation, and clamping of the workpiece. It generally needs to follow the following rules: the processing of the previous process cannot affect the positioning and clamping of the subsequent process
The machining process should start with rough machining and then finish machining, with machining allowance decreasing from large to small
First perform inner cavity processing, then proceed with outer contour processing
Minimize the number of tool changes and repeated positioning and clamping of workpieces as much as possible
3. Determination of processing technology and cutting methods
Tool selection: Choose appropriate tools for different machining processes and machining areas.
Selection of tool path form: A reasonable tool path trajectory can better ensure the quality and efficiency of machining.
Error control: Determine the error links and error control parameters related to programming.
Residual height control: Based on comprehensive considerations such as tool parameters, machining parameters, and machining surface requirements, strive to improve machining efficiency as much as possible.
Cutting process control: cutting quantity control, machining allowance control, advance and retreat tool control, cooling control, etc
Safety control: including safe height, avoidance zone, interference check, etc.
Process analysis planning is a flexible part of numerical control programming, which is influenced by multiple factors such as machine tools, cutting tools, and material properties. At the same time, it tests the programmers‘ grasp of experience, and the eternal pursuit of programmers is to successfully complete production under the premise of efficiency and safety.


 Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German French
French Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Korean
Korean Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latin
Latin Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Malay
Malay Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese 简体中文
简体中文 Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole