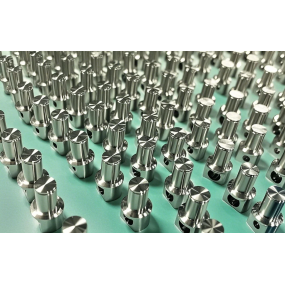
How to look at the technical level of a numerical control machine tool, the most intuitive feedback is its processing efficiency and repeated positioning accuracy, the repeated positioning accuracy of a machine tool is assumed to be able to achieve the 0.005mm standard, then this is a high-precision machine tool, but if the implementation of 0.005mm or less, that is ultra-high precision machine tool, machine tool accuracy in addition to the system, hardware also needs to have the best screw and bearing to match.

 When it comes to the "accuracy" of numerical control machine tools, it is necessary to clarify the definition of standards, indicators and calculation methods. When some numerical control machine tool manufacturers in Japan calibrate "accuracy", they usually use JISB6201 or JISB6336 or JISB6338 standards. JISB6201 is generally used for general-purpose machine tools and ordinary numerical control machine tools, JISB6336 is generally used for machining centers, and JISB6338 is generally used for vertical machining centers. The three standards mentioned above are basically the same when defining positional accuracy. We use JISB6336 as an example because on the one hand this standard is relatively new, and on the other hand it is slightly more accurate than the other two standards.
When it comes to the "accuracy" of numerical control machine tools, it is necessary to clarify the definition of standards, indicators and calculation methods. When some numerical control machine tool manufacturers in Japan calibrate "accuracy", they usually use JISB6201 or JISB6336 or JISB6338 standards. JISB6201 is generally used for general-purpose machine tools and ordinary numerical control machine tools, JISB6336 is generally used for machining centers, and JISB6338 is generally used for vertical machining centers. The three standards mentioned above are basically the same when defining positional accuracy. We use JISB6336 as an example because on the one hand this standard is relatively new, and on the other hand it is slightly more accurate than the other two standards.
European machine tool manufacturers, especially those in Germany and Switzerland, generally use the VDI/DGQ3441 standard. American machine tool manufacturers usually use the NMTBA (NationalMachineToolBuilder‘s Assn) standard (which originated from a study by the American Machine Tool Manufacturers Association and was promulgated in 1968 and later revised).
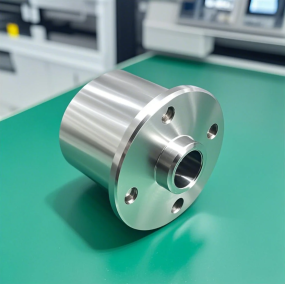
 The standards mentioned above are all related to ISO standards. For example, the dimensional accuracy and shape accuracy of typical parts machined by machining centers are compared at home and abroad. The domestic level is roughly 0.008~ 0.010mm, while the international advanced level is 0.002~ 0.003mm.
The standards mentioned above are all related to ISO standards. For example, the dimensional accuracy and shape accuracy of typical parts machined by machining centers are compared at home and abroad. The domestic level is roughly 0.008~ 0.010mm, while the international advanced level is 0.002~ 0.003mm.
Although the development of our country‘s machine tool manufacturing industry has ups and downs, but the numerical control technology and numerical control machine tools have been given greater attention, has a strong market competitiveness. However, in the middle and high-grade numerical control machine tools, with some foreign advanced products and technology development, there is still a big gap, most of them are in the technical tracking stage.
Ultra-precision machining currently refers to the size and position accuracy of 0.01~ 0.3μm, shape and contour accuracy of 0.003~ 0.1μm, surface roughness of steel Ra0.05μm, copper Ra0.01μm. The ultra-precision numerical control lathe and numerical control milling machine developed in China have been put into production. At present, it is necessary to develop ultra-precision grinding machines and ultra-precision composite machining machine tools in terms of varieties. At the same time, it is necessary to further improve the performance of ultra-precision spindle unit, ultra-precision guide rail sub-unit, ultra-precision smooth drive system, ultra-precision contour control technology and nano-resolution numerical control system and accelerate its engineering.
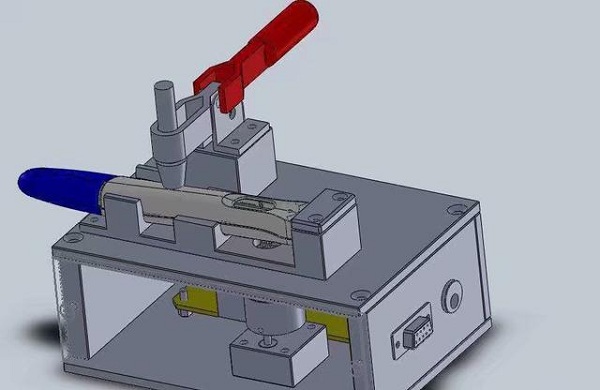
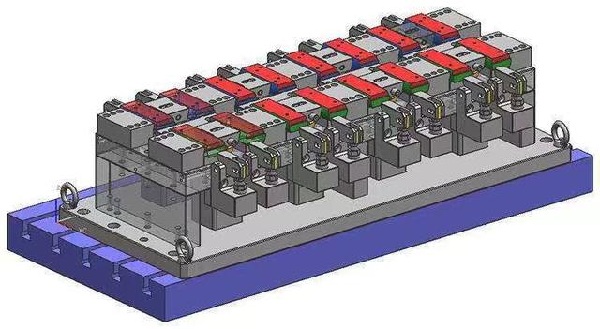
 Ultra-precision machine tools are mainly used to solve the ultra-precision machining of domestic high-tech and national defense key products. Although the demand is not very large, it is a sensitive technology blocked by foreign technology. On the other hand, the deepening research of ultra-precision machining technology will help the development and industrialization of high-precision machine tools that require a large amount of machining accuracy at the sub-micron level.
Ultra-precision machine tools are mainly used to solve the ultra-precision machining of domestic high-tech and national defense key products. Although the demand is not very large, it is a sensitive technology blocked by foreign technology. On the other hand, the deepening research of ultra-precision machining technology will help the development and industrialization of high-precision machine tools that require a large amount of machining accuracy at the sub-micron level.
Shenzhen EMAR Precision Technology Co., Ltd. is a professional dedicated to high-precision numerical control machine tool external processing strength manufacturers, the company has more than 100 high-precision numerical control machine tools, can provide lathes, milling machines, drilling machines, composite processing, cnc processing business, products cover medical, communications, optics, drones, robots, automobiles, office automation, the company successfully passed the IATF16949 quality management certification last year, in the realization of high-efficiency processing while the product accuracy control within 0.01mm.


 Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic French
French Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Malay
Malay Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Korean
Korean Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latin
Latin Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque