A car is composed of many parts, each part plays a different role, also need to be processed through different processing technology, and then can be installed on the car for use, auto parts processing What are the processes? Shenzhen EMAR Precision Technology focuses on high-precision numerical control machine tool external processing, its products also involve the field of auto parts, today we have taken stock of the seven processes of auto parts processing for you, let‘s take a look.
Forging and processing of automotive parts
In the process of automobile manufacturing, forging is widely used. Forging methods are divided into free forging and model forging. Free forging is a processing method in which a metal blank is placed on an anvil to withstand impact or pressure (known as "ironing"). Blanks such as gears and shafts of automobiles are processed by free forging.
 Model forging is a processing method in which a metal blank is placed in the die chamber of a forging die and formed by impact or pressure. Model forging is a bit like the process of dough being pressed into the shape of a cookie in a die. Compared with free forging, die forging produces workpieces with more complex shapes and more accurate dimensions. Typical examples of die forging for automobiles are: engine connecting rods and crankshafts, steering knuckles, front axles of automobiles, etc.
Model forging is a processing method in which a metal blank is placed in the die chamber of a forging die and formed by impact or pressure. Model forging is a bit like the process of dough being pressed into the shape of a cookie in a die. Compared with free forging, die forging produces workpieces with more complex shapes and more accurate dimensions. Typical examples of die forging for automobiles are: engine connecting rods and crankshafts, steering knuckles, front axles of automobiles, etc.
Second, automotive parts casting processing
Casting is a production method in which molten metal is poured into the mold cavity, cooled and solidified to obtain the product. In the manufacturing process of automobile parts, there are many parts made of cast iron, accounting for about 10% of the weight of the whole vehicle, such as cylinder block, transmission box, steering gear shell, rear axle shell, brake drum, various brackets, etc.
Sand molds are usually used in the manufacture of iron castings. The raw material of sand molds is mainly sand and mixed with binders, water, etc. The sand mold material must have a certain adhesive strength in order to be molded into the desired shape and resist the initialization of high-temperature molten iron without collapsing. In order to mold a cavity in the sand mold that matches the shape of the casting, a model must be made of wood first, called a wood mold. The volume of hot molten iron will shrink after cooling. Therefore, the size of the wood mold needs to be increased according to the shrinkage rate on the basis of the original size of the casting, and the surface that needs to be cut is thickened accordingly.
 Hollow castings need to be made into sand cores and corresponding core wood molds (core boxes). With the wood mold, the cavity sand mold (casting is also called "turning sand") can be turned. When making sand molds, consider how the upper and lower sand boxes are separated to remove the wood mold, and also consider where the molten iron flows in and how to fill the cavity to obtain a high-quality casting. After the sand mold is made, it can be poured, that is, molten iron is poured into the cavity of the sand mold. When pouring, the temperature of molten iron is 1250-1350 degrees, and the temperature is higher when melting.
Hollow castings need to be made into sand cores and corresponding core wood molds (core boxes). With the wood mold, the cavity sand mold (casting is also called "turning sand") can be turned. When making sand molds, consider how the upper and lower sand boxes are separated to remove the wood mold, and also consider where the molten iron flows in and how to fill the cavity to obtain a high-quality casting. After the sand mold is made, it can be poured, that is, molten iron is poured into the cavity of the sand mold. When pouring, the temperature of molten iron is 1250-1350 degrees, and the temperature is higher when melting.
III. Welding of automotive parts
Welding is the processing method of joining two pieces of metal together by local heating or simultaneous heating and pressure. We often see workers holding masks in one hand and welding tongs and electrodes connected to wires in the other. The welding method is called manual arc welding, which uses high-temperature arc discharge to melt electrodes and weldments and make them join.
Manual arc welding is not used much in automobile manufacturing. The most widely used in automobile body manufacturing is spot welding. Spot welding is suitable for welding thin steel plates. During operation, two electrodes apply pressure to two steel plates to make them stick and at the same time, the bonding point (a circle with a diameter of 5-6%) is heated and melted to firmly join. When welding two body parts, the edges of two body parts are welded every 50-100%, so that the two parts form a discontinuous multi-point connection. Welding the entire car body usually requires thousands of solder joints. The strength of the solder joints is very high. Each solder joint can withstand a tension of 5kN. Even if the steel plate is torn, the solder joint cannot be separated.
 Gas welding, which is common in repair shops, is a method of burning acetylene and using oxygen to support combustion to produce a high-temperature flame, which melts and joins the electrode and the weldment. This high-temperature flame can also be used to cut the metal, which is called gas cutting. Gas welding and gas cutting applications are more flexible, but the heat-affected zone of gas welding is larger, which causes deformation and metallographic structure changes of the weldment, and the performance is reduced. Therefore, gas welding is rarely used in automobile manufacturing.
Gas welding, which is common in repair shops, is a method of burning acetylene and using oxygen to support combustion to produce a high-temperature flame, which melts and joins the electrode and the weldment. This high-temperature flame can also be used to cut the metal, which is called gas cutting. Gas welding and gas cutting applications are more flexible, but the heat-affected zone of gas welding is larger, which causes deformation and metallographic structure changes of the weldment, and the performance is reduced. Therefore, gas welding is rarely used in automobile manufacturing.
Four, automotive parts cold stamping processing
Cold stamping or sheet Metal Stamping is a processing method in which sheet metal is cut or formed under pressure in a die. Daily necessities such as aluminum pots, lunch boxes, washbasins, etc. are made by cold stamping processing methods. For example, to make lunch boxes, it is first necessary to cut out a rectangular blank with 4 rounded corners (referred to in the industry as "blanking"), and then use a punch to press the blank into the concave mold to form (referred to in the industry as "drawing"). In the drawing process, the flat sheet becomes box-shaped, and its 4 sides are bent vertically upward. The material at the 4 corners is piled up and wrinkles can be seen.
 Auto parts processed by cold stamping include: engine oil pan, brake baseplate, car frame and most body parts. These parts are generally formed through processes such as blanking, punching, deep drawing, bending, flanging, and trimming. In order to manufacture cold stamped parts, a stamping die must be prepared. The stamping die is usually divided into two pieces, one of which is installed above the press and can slide up and down, and the other is installed under the press and fixed. During production, the blank is placed between the two stamping dies. When the upper and lower dies are closed, the stamping process is completed. The productivity of stamping processing is very high, and parts with complex shapes and high precision can be manufactured.
Auto parts processed by cold stamping include: engine oil pan, brake baseplate, car frame and most body parts. These parts are generally formed through processes such as blanking, punching, deep drawing, bending, flanging, and trimming. In order to manufacture cold stamped parts, a stamping die must be prepared. The stamping die is usually divided into two pieces, one of which is installed above the press and can slide up and down, and the other is installed under the press and fixed. During production, the blank is placed between the two stamping dies. When the upper and lower dies are closed, the stamping process is completed. The productivity of stamping processing is very high, and parts with complex shapes and high precision can be manufactured.
Cutting of automotive parts
Automotive parts cutting is the use of cutting tools to cut metal blanks layer by layer; so that the workpiece to the desired shape, size and surface roughness of the processing method. Metal cutting includes two methods of fitter and machining. Fitter is a processing method for workers to cut with hand tools. It is flexible and convenient to operate and is widely used in assembly and repair. Machining is the use of machine tools to complete cutting, including: turning, planing, milling, drilling and grinding methods.
 1. Planning:
1. Planning:
Planing is the process of machining a workpiece with a planer. Planers are suitable for machining horizontal, vertical, inclined and grooves, etc. Cylinder blocks and cylinder heads on automobiles, and matching planes of transmission boxes and covers are all machined with planers.
2. Turning:
Turning is the process of machining a workpiece with a turning tool on a lathe. A lathe is suitable for cutting various rotating surfaces, such as inner and outer cylinders or conical surfaces, and can also turn end faces. Many shaft parts and gear blanks of automobiles are machined on a lathe.
3. Milling:
Milling is the process of machining workpieces with a milling cutter on a milling machine. Milling machines can process inclined surfaces, grooves, and even gears and curved surfaces. Old milling is widely used to process various automotive parts. The dies for cold stamping of automobile bodies are all processed by milling. Computer-operated numerical control milling machines can process workpieces with complex shapes and are the main machine tools for modern machining.
4. Grinding:
Grinding is the process of machining a workpiece with a grinding wheel on a grinder. Grinding is a finishing method that can obtain workpieces with high precision and roughness, and can grind workpieces with high hardness. Some heat-treated automotive parts are finished with a grinder.
5. Drilling and boring:
Drilling and boring are the main cutting methods for hole machining.
Six, automotive parts heat treatment processing
Heat treatment is the method of reheating, holding or cooling solid steel to change its organizational structure to meet the requirements of parts or process requirements. The level of heating temperature, the length of holding time, and the speed of cooling can cause different structural changes in steel. Blacksmiths immerse heated steel parts in water for rapid cooling (experts call quenching), which can improve the hardness of steel parts. This is an example of heat treatment.
 Heat treatment processes include annealing, normalizing, quenching and tempering, etc. Annealing is the process of heating steel parts, holding them for a certain period of time, and then slowly cooling them together with the furnace to obtain a finer and uniform structure, reduce hardness, and facilitate cutting. Normalizing is the process of heating steel parts, taking them out of the furnace after holding them warm, and then cooling them in air, which is suitable for refining low carbon steel. Quenching is the process of heating steel parts, and then cooling them quickly in water or oil after holding them warm to improve hardness. Tempering is usually the follow-up process of quenching. The quenched steel parts are reheated and cooled after holding them warm to stabilize the structure and eliminate brittleness. There are many automotive parts that require surface high-frequency quenching or carburizing, cyanidation, and other heat treatment processes to preserve the toughness of the core while altering the surface structure to improve hardness.
Heat treatment processes include annealing, normalizing, quenching and tempering, etc. Annealing is the process of heating steel parts, holding them for a certain period of time, and then slowly cooling them together with the furnace to obtain a finer and uniform structure, reduce hardness, and facilitate cutting. Normalizing is the process of heating steel parts, taking them out of the furnace after holding them warm, and then cooling them in air, which is suitable for refining low carbon steel. Quenching is the process of heating steel parts, and then cooling them quickly in water or oil after holding them warm to improve hardness. Tempering is usually the follow-up process of quenching. The quenched steel parts are reheated and cooled after holding them warm to stabilize the structure and eliminate brittleness. There are many automotive parts that require surface high-frequency quenching or carburizing, cyanidation, and other heat treatment processes to preserve the toughness of the core while altering the surface structure to improve hardness.
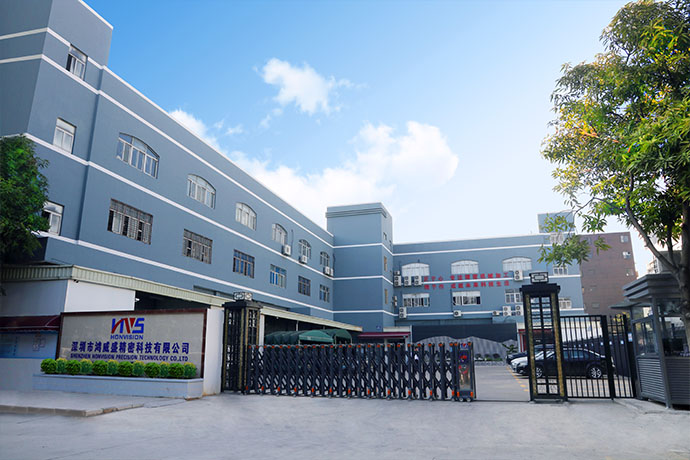 Shenzhen EMAR Precision Technology Co., Ltd. has more than ten years of experience in precision machining, based in the medical, communications, optoelectronic industry, the current products involved in addition to automotive parts processing, but also includes aerospace, intelligent machine, optical and other precision parts customization and batch processing, the company has modern precision numerical control equipment, including central numerical control lathe, knife type numerical control lathe, turn-milling composite machining center and four-axis, five-axis linkage vertical machining center processing, and the company successfully passed the IATF16949 quality management certification last year, is a manufacturer with automotive parts processing qualifications and processing strength.
Shenzhen EMAR Precision Technology Co., Ltd. has more than ten years of experience in precision machining, based in the medical, communications, optoelectronic industry, the current products involved in addition to automotive parts processing, but also includes aerospace, intelligent machine, optical and other precision parts customization and batch processing, the company has modern precision numerical control equipment, including central numerical control lathe, knife type numerical control lathe, turn-milling composite machining center and four-axis, five-axis linkage vertical machining center processing, and the company successfully passed the IATF16949 quality management certification last year, is a manufacturer with automotive parts processing qualifications and processing strength.


 Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic French
French Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Malay
Malay Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Korean
Korean Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latin
Latin Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque