Cabinet processing is a more complex metal processing technology. The following is the relevant introduction: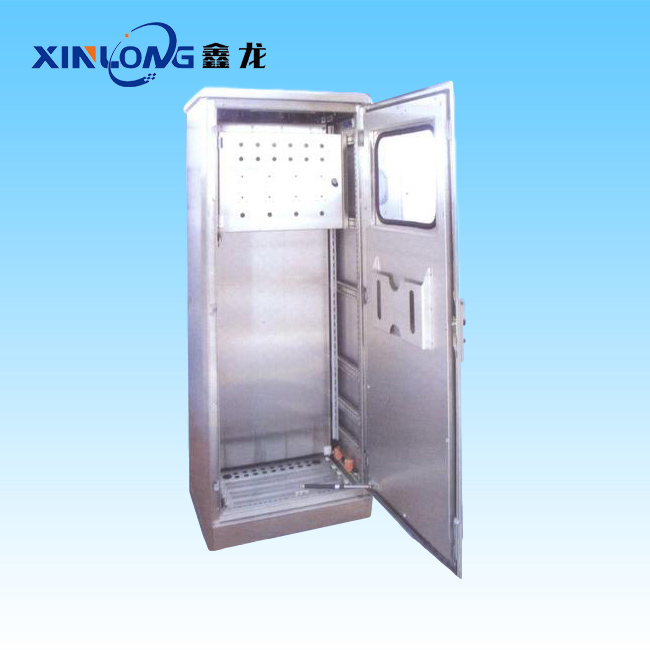  Design: According to customer needs and equipment specifications, design the size, structure, layout, etc. of the cabinet, and make detailed drawings and process documents, including determining the external dimensions of the cabinet, the division of internal space, the location and connection of each component, etc. Material preparation: According to the design requirements, prepare suitable metal plates and parts. Common materials include cold-rolled steel plates, stainless steel plates, aluminum alloys, etc., and check whether the quality and specifications of the materials meet the requirements. Cutting: using cutting tools, such as laser cutting machines, numerical control punches, etc., to cut plates and parts into the desired shape and size, this process should ensure cutting accuracy, control the roughness and flatness of the cutting surface. Bending: through bending machines and other tools, the cut plates are bent into the designed shape, and the appropriate bending angle and radius should be selected according to the material characteristics and design requirements to avoid problems such as cracks or deformation. Splicing: The bent parts are spliced and assembled, and welding, bolting, riveting, etc. can be used to ensure a firm connection and ensure the overall structural strength and stability of the cabinet. Calibration: Use measuring tools to calibrate the size and shape of the spliced cabinet, check the positional accuracy and flatness of each component, and adjust and correct the parts that do not meet the requirements. Grinding: Grind the surface of the cabinet to remove burrs, sharp edges and welding marks, etc., to make the surface smooth and flat, improve the appearance quality and safety of the cabinet. Spraying: In order to prevent rust and corrosion of the cabinet and enhance its aesthetics, it is necessary to spray the surface, choose painting, spraying, etc., and choose the appropriate paint color and coating thickness according to different use environments and requirements. Inspection: Conduct a comprehensive quality inspection of the processed cabinets, including appearance inspection, dimensional accuracy measurement, structural strength testing, electrical performance testing, etc., to ensure that the products meet relevant standards and customer requirements. Packaging: Pack the cabinets that have passed the inspection, and choose the appropriate packaging materials and methods, such as wooden box packaging, foam packaging, etc., to prevent damage during transportation and storage.
Design: According to customer needs and equipment specifications, design the size, structure, layout, etc. of the cabinet, and make detailed drawings and process documents, including determining the external dimensions of the cabinet, the division of internal space, the location and connection of each component, etc. Material preparation: According to the design requirements, prepare suitable metal plates and parts. Common materials include cold-rolled steel plates, stainless steel plates, aluminum alloys, etc., and check whether the quality and specifications of the materials meet the requirements. Cutting: using cutting tools, such as laser cutting machines, numerical control punches, etc., to cut plates and parts into the desired shape and size, this process should ensure cutting accuracy, control the roughness and flatness of the cutting surface. Bending: through bending machines and other tools, the cut plates are bent into the designed shape, and the appropriate bending angle and radius should be selected according to the material characteristics and design requirements to avoid problems such as cracks or deformation. Splicing: The bent parts are spliced and assembled, and welding, bolting, riveting, etc. can be used to ensure a firm connection and ensure the overall structural strength and stability of the cabinet. Calibration: Use measuring tools to calibrate the size and shape of the spliced cabinet, check the positional accuracy and flatness of each component, and adjust and correct the parts that do not meet the requirements. Grinding: Grind the surface of the cabinet to remove burrs, sharp edges and welding marks, etc., to make the surface smooth and flat, improve the appearance quality and safety of the cabinet. Spraying: In order to prevent rust and corrosion of the cabinet and enhance its aesthetics, it is necessary to spray the surface, choose painting, spraying, etc., and choose the appropriate paint color and coating thickness according to different use environments and requirements. Inspection: Conduct a comprehensive quality inspection of the processed cabinets, including appearance inspection, dimensional accuracy measurement, structural strength testing, electrical performance testing, etc., to ensure that the products meet relevant standards and customer requirements. Packaging: Pack the cabinets that have passed the inspection, and choose the appropriate packaging materials and methods, such as wooden box packaging, foam packaging, etc., to prevent damage during transportation and storage.
Hello! Welcome to EMAR's website!
 English
English » »
» »
 Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic French
French Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Malay
Malay Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Korean
Korean Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latin
Latin Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque