With the increasing popularity of metal body smartphones, words related to metal body processing technology such as CNC, stamping, forging, die-casting, and so on have become more and more frequent. Below is a detailed introduction to several commonly used processing methods for metal body in mobile phones.
1. Casting
Metal casting is the process of injecting molten metal into a hollow mold made of high-temperature resistant materials, condensing it to obtain the desired shape of the product, and the resulting product is the casting.
Metal casting can be divided into gravity casting and pressure casting based on whether it is affected by pressure. Gravity casting refers to the process of injecting molten metal into a mold under the influence of Earth's gravity, also known as casting; The metal liquid is generally poured manually into the gate, relying on the self weight of the metal liquid to fill the mold cavity, exhaust, cool, and open the mold to obtain the product. Pressure casting refers to the method of filling the cavity of a die casting mold with liquid or semi liquid metal at a high speed under high pressure, and forming and solidifying under pressure to obtain castings. The Meilan metal released by Meizu adopts high-pressure casting followed by spray coating treatment.

Meilan Metal
2. Forging
Forging refers to a machining process that uses pressure to change the shape of metal raw materials in order to obtain forgings with certain mechanical properties, shape, and size.
Metal forging can be divided into five types based on the different tools used for pressurization: hammer forging, drop hammer forging, pressure forging, end pressure forging, and rolling forging. Hammer pressing refers to heating the workpiece to forging temperature and forging it between a flat hammer and a drilling plate; Small pieces can be called iron by hand; Large items require the use of a steam hammer. The difference between drop hammer forging and flat forging lies in the fact that the hammer in drop hammer forging has a die cavity, in which the working piece bears two types of pressure or impact forces, and then undergoes plastic deformation according to the shape of the die cavity. Pressure forging is a forging method that uses slow pressure to squeeze metal into shape in the mold. Due to the long time the metal is subjected to force, the squeezing effect not only occurs on the surface of the forging, but also on the central part of the workpiece, achieving a uniform effect inside and outside. For example, the R7 mobile phone case of OPPO is made by pressure forging followed by surface anodizing treatment.

OPPO r7
3. Punching
Stamping refers to the direct force forming of metal sheets in a mold using the power of stamping equipment. It is a metal cold treatment processing method, also known as cold stamping or sheet metal stamping. The process flow can be roughly divided into three steps: first, fix the metal plate on the mold table, then the upper punch falls vertically to form the metal plate under force inside the mold, and finally the punch rises. The parts are taken out and wait for the next edge trimming and polishing process. The entire process takes about 1s-1min. Xiaomi's Redmi Note 3 is a metal back cover made using stamping technology.

Red Rice Note3
4 CNC process
CNC, The full name is Computer Numerical Control, which refers to an automated machine tool controlled by a program, commonly known as a "CNC machine tool". This control system is capable of logically processing programs with control codes or other symbolic instructions. Through computer decoding, the machine tool executes predetermined actions, and through long-term precision machining, a raw metal sheet is ultimately shaped into the desired shape. Starting from the iPhone 5, Apple has adopted aluminum alloy integrated molding, with the body and frame made of a single piece of aluminum alloy CNC Machining.

iPhone 6
What kind of processing technology is used for the metal casing of mobile phones, and its processing cost The amount of CNC used, processing cycle, yield, designability, and appearance texture are closely related, and these influencing factors can form a process radar chart. The larger the area of a process radar chart, the better its overall performance; From a single dimension analysis, each dimension is divided into 10 levels, and the higher the score, the better a certain process is in that dimension.
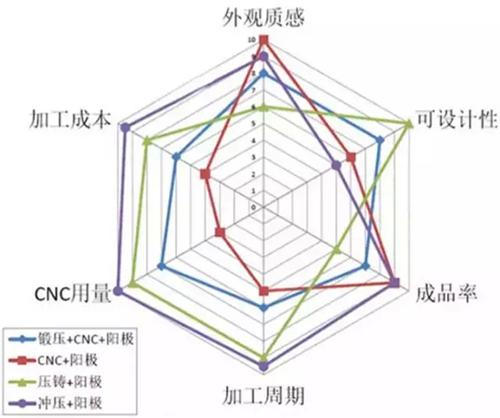
Process radar diagram


 Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic French
French Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Malay
Malay Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Korean
Korean Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latin
Latin Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque











