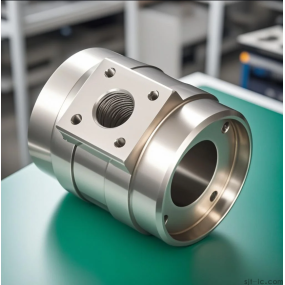
Four processing stages of CNC prototype model making process
 When the surface accuracy and roughness requirements of a part are relatively high, it is often impossible to complete the processing in one process, and it is divided into several stages for processing.
When the surface accuracy and roughness requirements of a part are relatively high, it is often impossible to complete the processing in one process, and it is divided into several stages for processing.
1.Four processing stages of the CNC prototype model making process
(1) Roughing stage. Roughing is mainly to remove most of the machining allowance on each surface, so that the shape and size of the blank are close to the finished product. This stage is characterized by the use of high-power machine tools and the selection of larger cutting tools to improve productivity and reduce tool wear as much as possible.
(2) Semi-finishing stage. Semi-finishing is to complete the processing of secondary surfaces and prepare for the finishing of major surfaces.
(3) Finishing stage. Finishing is the process of ensuring that the main surface meets the requirements of the pattern.
(4) Finishing stage. Finishing is a surface that requires high surface roughness and machining accuracy, and requires finishing. This stage generally cannot be used to improve the positional accuracy of parts.
It should be pointed out that the division of the processing stage is based on the entire process of parts processing, and cannot be judged by the processing of a surface or the nature of a certain process. At the same time, in specific applications, it cannot be absolute. For some heavy parts or parts with small margin and low precision, rough finishing of the surface can be completed after one clamping.


 Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic French
French Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Malay
Malay Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Korean
Korean Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latin
Latin Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque