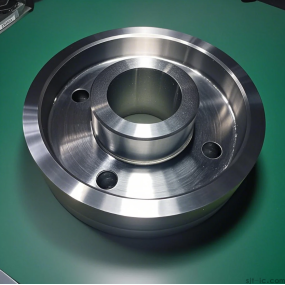
First, stamping equipment and die tooling management. The stamping workshop implements WCM-PM management on end pickup and die management, including equipment ledger, fault analysis, spare parts management, and formulates monthly inspection and maintenance plans according to the monthly production plan, as well as end pickup and die changes. The tooling die implements regular maintenance, implements a mandatory pre-repair system, maintains according to the number of times the die is punched, and establishes a maintenance standard frequency. Establish a quality maintenance matrix to show the relationship between quality key points and die part parameters through the matrix. Control the mold parameters, process parameters and equipment parameters used in production to ensure the quality of stamped parts. The mold parameters in the production process include knife edge clearance, mold nitrogen cylinder pressure, blank limit size, etc. These parameters need to be specified in the mold maintenance work instructions; the process parameters are generally determined by the mold itself, mainly including the mold mounting height, closing height, hydraulic pad stroke, hydraulic pad pressure, balancer pressure and ejector rod specifications. This information needs to be clarified in the "Mold Installation Card". If the relevant parameters need to be changed, the quality personnel will confirm that during the mold debugging process, the operator will set according to the requirements of the parts processing technology. During the process, the stamping workshop quality inspector will check the conformity of the parameters before each batch of production and keep records. Equipment parameters mainly include table parallelism, table verticality, slider parallelism, slider verticality, hydraulic pad tonnage accuracy, balance air pressure accuracy, etc. If there is a deviation in these parameters, it will seriously affect the quality of stamping parts. These parameters require equipment technicians to measure and monitor regularly. For stamping workshops, it is generally tested once a quarter. Second, the main points of stamping die forging steps. The smooth implementation of stamping die forging process also requires production personnel to reasonably grasp the production steps and stamping methods of stamping die manufacturing. 1. The processing methods of stamping die, stamping die processing methods, are mainly divided into natural stamping and molding stamping forging. Natural stamping means that when the production staff produces the stamping die, they can directly press the stamping process according to the formation style of the stamping material blank design, without the need to adjust the forging material again during the forging process. And modular stamping forging means that during the forging production of the stamping model, the forging process needs to be adjusted on the initially formed model according to the regulations of the model production. For example, during the forging production of rigid-bonded cemented carbide, after the forging process in the blank processing link is completed, the model cutting and embossing treatment can be directly carried out in the follow-up; while aluminum-copper alloy, after the processing in the blank stage, it is also necessary to adjust the model angle, thickness, curvature and other aspects during the later forging production. This is the difference between natural stamping and molding stamping methods. 2. Processing steps of stamping die. During the forging practice of stamping die, construction personnel need to grasp the steps of product production. At present, the steps in the practice of stamping die manufacturing technology mainly include forward processing and reverse processing. The forward processing process refers to the adjustment of the forging model at the position of 2/3 of the forging surface in combination with the fiber direction of the original blank, carbonization treatment, and then processing according to the die part of the stamping part. The reverse processing method refers to the vertical direction of the blank, from the bottom of the model to the top of the forging process, and pay special attention to the treatment of the convex belly crack part, and control the adjustment angle within 900, focusing on die processing.
Hello! Welcome to EMAR's website!
 English
English » »
» »
 Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic French
French Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Malay
Malay Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Korean
Korean Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latin
Latin Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque